The association between magnesium depletion score (MDS) and overactive bladder (OAB) among the U.S. population
- PMID: 40181471
- PMCID: PMC11969968
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-025-00846-x
The association between magnesium depletion score (MDS) and overactive bladder (OAB) among the U.S. population
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the relationship between magnesium depletion score (MDS) and overactive bladder (OAB) prevalence.
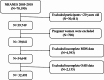
Methods: This study utilized data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2005 to 2018. Multivariate logistic regression was employed to investigate the association between MDS and OAB. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis explored the linear or non-linear relationship between MDS and OAB. Interaction analyses were conducted on subgroups to validate the findings.
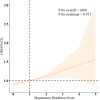
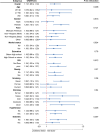
Results: There was a significant positive association between MDS and OAB. After adjusting for covariates, with each unit increase in MDS, there was an 11% increase in the prevalence of infertility (P < 0.001). In addition, the incidence of OAB was significantly increased in the higher MDS group compared to the low MDS group (MDS = 0) (P for trend < 0.001). The dose-response curve indicated a linear association between MDS and OAB, with higher MDS associated with higher OAB.
Conclusion: The results of this study show a strong positive correlation between MDS and the prevalence of OAB. These findings suggest that monitoring and managing magnesium status may be a potential strategy for reducing the risk of OAB.
Keywords: Association; Magnesium depletion score; NHANES; Overactive bladder; U.S. Population.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The data survey conducted by NHANES has been approved by the NCHS Research Ethics Review Board (ERB). All information from the NHANES program is available and free for the public, so an individual investigator was not necessary to obtain approval from the institution’s internal ethics review board. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Henderson E, Drake M. Overactive bladder. Maturitas. 2010;66:257–62. - PubMed
-
- Andersson K-E, Arner A. Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:935–86. - PubMed
-
- de Groat WC. A neurologic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology. 1997;50:36–52. discussion 53–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

