Study on the efficacy of IFN-γ- and sPD-1-overexpressing BMSCs in enhancing immune effects for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40181963
- PMCID: PMC11965897
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1554467
Study on the efficacy of IFN-γ- and sPD-1-overexpressing BMSCs in enhancing immune effects for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Soluble programmed cell death receptor-1 (sPD-1) blocks the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, reverses tumor immune suppression, and inhibits tumor growth. However, clinical applications are limited by its poor tissue distribution and rapid dispersion. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) are favorable carriers for tumor immunotherapy due to their capacity for external gene introduction and targeted tumor homing. However, they may inadvertently promote tumor growth. Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) inhibits BMSC-mediated tumor growth and stimulates antigen-presenting cells to activate T lymphocytes. This study utilizes BMSCs transfected with IFN-γ as carriers for sPD-1, enabling the targeted homing of sPD-1 to tumor tissues, thereby enhancing the efficacy and sustained stability of immunotherapy.
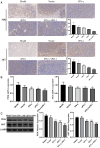
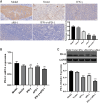
Methods: stable IFN-γ- and sPD-1-overexpressing BMSCs were successfully constructed by lentiviral transfection. A non-contact co-culture system was established with Lewis and A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells to observe changes in the lung cancer cells after co-culture, using assays including cell migration and invasion experiments, as well as cellular senescence detection. Additionally, a subcutaneous lung adenocarcinoma model was established in C57BL/6J mice for intervention studies. Tumor volume, cellular apoptosis in tumor tissue (assessed by TUNEL assay), peripheral Treg cells (analyzed by flow cytometry), and histopathological markers (evaluated by HE staining and immunohistochemistry) were analyzed. The expression levels of BAX, BCL-2, AKT, PI3K, and PD-L1 were assessed by quantitative PCR and Western Blot.
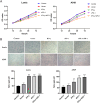
Results: IFN-γ- and sPD-1-overexpressing BMSCs exhibited high bioactivity and genetic stability, inhibiting lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, accelerating cellular senescence, and reducing migration and invasion. Furthermore, they upregulate Bax expression, downregulate Bcl-2, and promote apoptosis. Additionally, these cells alleviate inflammatory damage in lung tissue of tumor-bearing mice, lower Treg cell levels to inhibit tumor immune evasion, and reduce the expression of PI3K/AKT and PD-L1.
Conclusion: IFN-γ- and sPD-1-overexpressing BMSCs effectively inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell growth and tumor progression. The primary mechanisms include suppression of cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion; promotion of apoptosis and senescence in cancer cells; modulation of Treg cells; and inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and PD-1/PD-L1 pathways.
Keywords: BMSCs; IFN-γ; immune suppression; lung adenocarcinoma; sPD-1.
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Lv, Wang, Ma, Wei, Zheng and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ancin B, Ozercan MM, Yilmaz YM, Uysal S, Kumbasar U, Saribas Z, et al. The correlation of serum spd-1 and spd-L1 levels with clinical, pathological characteristics and lymph node metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients. Turk J Med Sci. (2022) 52:1050–7. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5407 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

