Demethylase FTO mediates m6A modification of ENST00000619282 to promote apoptosis escape in rheumatoid arthritis and the intervention effect of Xinfeng Capsule
- PMID: 40181982
- PMCID: PMC11966437
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1556764
Demethylase FTO mediates m6A modification of ENST00000619282 to promote apoptosis escape in rheumatoid arthritis and the intervention effect of Xinfeng Capsule
Abstract
Introduction: The pathological mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are closely associated with the apoptosis escape of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). The m6A modification of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) plays a critical regulatory role in RA pathogenesis. Xinfeng Capsule (XFC), a clinically effective traditional Chinese medicine formulation, has been shown to alleviate RA by inhibiting FLS apoptosis escape. However, its molecular mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to elucidate the mechanism by which the demethylase FTO promoted FLS apoptosis escape through the m6A modification of lncRNA ENST00000619282 and to reveal the therapeutic targets of XFC in treating RA by intervening in this m6A-dependent pathway.
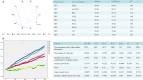
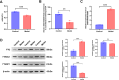
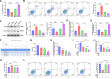
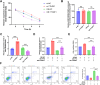
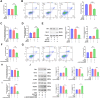
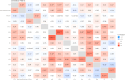
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 1603 RA patients using association rule mining and random walk algorithms to evaluate the efficacy of XFC. The proliferation and apoptosis of co-cultured RA-FLS were assessed using CCK-8, flow cytometry (FCM), and molecular biology techniques. Bioinformatics prediction, MeRIP-qPCR, RIP, and RNA pull-down assays were employed to identify the m6A modification sites of ENST00000619282 and their interactions with FTO/YTHDF1. Additionally, FISH, luciferase reporter assays, and rescue experiments were performed to validate the regulatory role of ENST00000619282 and its sponge-like function in RA-FLS. Clinical samples were analyzed to determine the correlation between FTO/YTHDF1/ENST00000619282/Bax/Bcl-2 and immune-inflammatory markers. Furthermore, the binding affinity of XFC active components to NF-κB was assessed through molecular docking.
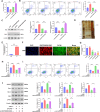
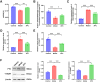
Results: Retrospective data mining demonstrated that XFC significantly improved immune-inflammatory markers in RA patients. Mechanistically, FTO reduced the m6A modification level of ENST00000619282, enhancing its stability and promoting YTHDF1-dependent expression, which in turn inhibited PUF60 and activated the NF-κB pathway, ultimately leading to FLS apoptosis escape. XFC downregulated FTO, increased the m6A modification of ENST00000619282, blocked the NF-κB signaling, inhibited RA-FLS proliferation, as well as induced their apoptosis. Clinical validation revealed that FTO/YTHDF1/ENST00000619282/Bax/Bcl-2 was closely associated with immune-inflammatory markers in RA patients. After XFC treatment, FTO, ENST00000619282, and Bcl-2 expressions were decreased, while YTHDF1 and Bax expressions were increased (all P<0.05). Molecular docking confirmed that the active components of XFC (calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, calycosin, and formononetin) exhibited strong binding affinity to NF-κB p65.
Conclusion: FTO promoted FLS apoptosis escape and RA progression by activating the NF-κB pathway through the m6A-dependent ENST00000619282/YTHDF1 axis. XFC inhibited this pathway by modulating FTO-mediated m6A modification, providing a novel RNA epigenetic regulatory strategy for RA treatment.
Keywords: ENST00000619282; FTO; M6A; Xinfeng Capsule; apoptosis escape; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wen, Liu, Xin, Fang, Sun and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
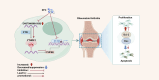
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Xinfeng Capsules-containing serum on TNF-α-induced apoptosis and inflammation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jan;46(2):436-443. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200915.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33645133 Chinese.
-
[Xinfeng Capsule alleviates RA-FLS-induced angiogenesis in HUVEC cells by inhibiting the lncRNA HOTAIR/PI3K/AKT pathway].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec;40(12):1057-1066. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39750043 Chinese.
-
[Serum from Xinfeng Capsule-treated rats affect the proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating circular RNA Cbl proto-oncogene B (circ-CBLB)].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Sep;40(9):792-799. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39442967 Chinese.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase gene BIRC3 modulates TNF-induced cell death pathways and promotes aberrant proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1433898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433898. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in nanodelivery systems based on apoptosis strategies for enhanced rheumatoid arthritis therapy.Acta Biomater. 2025 May 1;197:87-103. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.03.043. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40154765 Review.
Cited by
-
m6A modification of non‑coding RNA: Mechanisms, functions and potential values in human diseases (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Oct;56(4):164. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5605. Epub 2025 Aug 8. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40776750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of m6A-related lncRNAs as prognosis factors in the immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;16(3):986-1000. doi: 10.21037/jgo-2024-878. Epub 2025 Jun 27. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40672065 Free PMC article.
-
New Generation of Clinical Epigenetics Analysis and Diagnosis for Precision Medicine.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 17;15(12):1539. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121539. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Humby F, Durez P, Buch MH, Lewis MJ, Rizvi H, Rivellese F, et al. . et al: Rituximab versus tocilizumab in anti-TNF inadequate responder patients with rheumatoid arthritis (R4RA): 16-week outcomes of a stratified, biopsy-driven, multicentre, open-label, phase 4 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2021) 397:305–17. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32341-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

