Enhanced Absorption and Safety of MuscleBlaze CreAMP™: A Comparative Analysis With Regular Micronized Creatine Monohydrate in Healthy Male Adults
- PMID: 40182172
- PMCID: PMC11966180
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81555
Enhanced Absorption and Safety of MuscleBlaze CreAMP™: A Comparative Analysis With Regular Micronized Creatine Monohydrate in Healthy Male Adults
Abstract
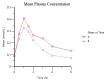
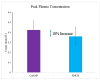
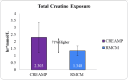
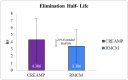
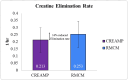
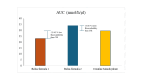
Background Creatine monohydrate is a widely utilized dietary supplement in sports nutrition, valued for its role in enhancing muscle energy availability, power output, and performance during high-intensity, short-duration activities. Creatine monohydrate is effective but limited by absorption inefficiencies and side effects. Enhanced forms can improve uptake, reduce gastrointestinal discomfort, and optimize muscle energy utilization, meeting athletes' evolving performance needs. Methods This study involved 32 healthy male volunteers aged 18-50 years, with a BMI of 18.5-25.0 kg/m² and body weight of ≥50 kg. This study evaluated the bioavailability and safety of MuscleBlaze Creatine Monohydrate (CreAMP™) (Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd, Gurugram, India), containing 3.0 g creatine monohydrate and 0.1 g Creabsorb™ (Indian Patent: IN202311057466), against a standard 3.0 g micronized creatine dose. In a double-blind, randomized crossover trial (CTRI/2024/08/073021), 32 healthy males (18-50 years) received both formulations under fasting conditions. The study compared two oral creatine monohydrate formulations: CreAMP™ Micronized Creatine Monohydrate (test) and Regular Micronized Creatine Monohydrate (reference) (Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd, Gurugram, India). Blood samples were collected pre-dose and up to six hours post-dose over two periods, separated by a washout period of one week. Pharmacokinetic parameters were analyzed using Phoenix® WinNonlin® 8.5 (Certara, Radnor, PA). Results CreAMP™ has significantly higher bioavailability, absorption, and plasma retention compared to the reference formulation. With a 38.97% increase in bioavailability, an 18.10% higher Cmax, a 21.37% longer half-life, 34.67% lower clearance, and a 10.13% higher mean residence time, CreAMP™ demonstrates superior pharmacokinetic properties. These findings suggest that CreAMP™ offers improved creatine uptake, sustained plasma levels, and the potential for reduced dosing frequency, making it a more effective formulation for creatine supplementation. Conclusion The study findings establish CreAMP™ as a superior creatine formulation, offering enhanced bioavailability, faster absorption, and prolonged plasma retention. These pharmacokinetic advantages indicate that CreAMP™ offers more efficient creatine uptake, improved energy availability, and optimized performance support for athletes.
Keywords: absorption; bioavailability; creamp™; muscle energy; performance; pharmacokinetics; s: : creatine monohydrate; safety; sports nutrition; supplementation.
Copyright © 2025, Trehan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Asopa Ethics Committee issued approval ECR/1581/Inst/RJ/2021. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: The trial was sponsored by Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd. No conflict of interest from all authors. Financial relationships: All authors declare(s) employment from Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd. All authors are employees of Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd. Intellectual property info: Creabsorb™ is a patent pending formula of Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd, having an application number mentioned in brackets (Indian Patent: IN202311057466). Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures



References
-
- Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:1107–1213. - PubMed
-
- Clinical pharmacology of the dietary supplement creatine monohydrate. Persky AM, Brazeau GA. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11356982/ Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:161–176. - PubMed
-
- Effects of creatine supplementation and resistance training on muscle strength and weightlifting performance. Rawson ES, Volek JS. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14636102/ J Strength Cond Res. 2003;17:822–831. - PubMed
-
- Effects of creatine supplementation on body composition, strength, and sprint performance. Kreider RB, Ferreira M, Wilson M, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14636102/ Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30:73–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
