Tolerability of facemask during physical exercises during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review
- PMID: 40182319
- PMCID: PMC11966696
- DOI: 10.4102/jphia.v16i2.610
Tolerability of facemask during physical exercises during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Available evidence supports the use of facemasks by all groups to prevent respiratory infections, particularly severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). However, it is not clear whether these masks can be used safely during various intensities of physical exercise.
Aim: To evaluate the impact of different types of facemasks on oxygen saturation, oxygen uptake, rate of perceived exertion and performance during different physical exercises.
Setting: Healthcare databases.
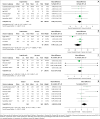
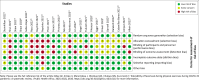
Method: We searched for articles published between 2020 to 05 September 2022. There was no restriction in age, language or setting. Electronic databases including The Cochrane Library - Central Register of Controlled Trials and Cochrane Database of systematic review and EPOC; MEDLINE; EMBASE were searched for articles for the period stated above. Risk of Bias in included studies was assessed using Cochrane risk of bias tool for RCTs.
Results: Twenty-four randomised control trials with cross-over design were included. There was a total of 617 participants (373 males and 244 females). None of studies reported on prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection by mask. The pooled effect estimate shows that wearing surgical mask did not affect oxygen saturation and oxygen uptake. Masks are tolerated during mild and moderate exercise, but reduce maximal exercise capacity. Children tolerate masks for submaximal exercise better than adults.
Conclusion: During physical exercises, masks should be used with caution by healthy adults and children but should be avoided by elderly and ill patients.
Contribution: This review offers current evidence on tolerability of facemask during physical exercises.
Keywords: SARS-CoV2; during physical activity; infection; masks; prevention.
© 2025. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported receiving funding from a grant from Country Readiness Strengthening, WHO World Health Emergencies Programme, Geneva, Switzerland, to Cochrane Nigeria, which may be impacted by the research presented in the enclosed publication. The author has fully disclosed these interests and has implemented an approved plan to manage any potential conflicts arising from their involvement. The terms of these funding arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the affiliated university in accordance with its policy on objectivity in research.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO health emergency dashboard (COVID-19). Geneva: WHO; 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
