Real-world outcomes of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in intermediate- and poor-risk metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40182649
- PMCID: PMC11964907
- DOI: 10.37349/etat.2025.1002305
Real-world outcomes of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in intermediate- and poor-risk metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
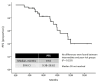
The combination of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab (Len + Pembro) demonstrated significant efficacy in the phase 3 CLEAR study for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, poor-risk patients represented only a small proportion of the trial population. This multicenter retrospective cohort study assessed the real-world efficacy and safety of Len + Pembro in patients with clear-cell metastatic RCC and intermediate or poor International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium risk. Outcomes included objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. Sixty patients were analyzed, with a median age of 56 years. Poor risk was identified in 53% of patients, and 90% had metastases to ≥ 2 organs. ORR was 48.33%, disease control rate was 86.7%, and median PFS was 19.0 months. Grade ≥ 3 adverse events occurred in 25% of patients, with 33.3% requiring lenvatinib dose reductions. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab demonstrated robust efficacy and a manageable safety profile in a real-world population with advanced disease and poor-risk features, consistent with outcomes reported in clinical trials.
Keywords: IMDC intermediate and poor risk; Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab; real-world evidence.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Eto M, Motzer R, Giorgi UD, Buchler T, Basappa NS, et al. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus sunitinib as first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (CLEAR): extended follow-up from the phase 3, randomised, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:228–38. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00049-9. Erratum in: Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:e146. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources