Parishin A ameliorates cognitive decline by promoting PS1 autophagy in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40182757
- PMCID: PMC11965357
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1516190
Parishin A ameliorates cognitive decline by promoting PS1 autophagy in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disease in the elderly. Its pathological features include: A lot of misfolding and abnormal aggregation of amyloid protein (Aβ); Autophagy disorder, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, abnormal phosphorylated tau protein and synaptic dysfunction. Modern pharmacological studies have found that Paisinhin A (PA) has beneficial effects on the prevention and treatment of central nervous system diseases. This study aims to explore the role and mechanism of PA in AD through autophagy pathway, and lay a scientific foundation for the development of clinical prevention and treatment strategies for AD.
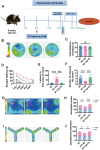
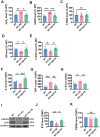
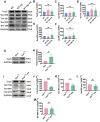
Methods: N2AAPP cells were treated with different concentrations of PA. Cell viability was detected by CCK-8 method. Western blotting detected the expression levels of proteins related to amyloid production, autophagy pathway, and phosphorylated Tau expression levels. Autophagy flow was detected by transfecting Lc3 double fluorescent plasmid. After Aβ was injected into the hippocampus of WT mice and PA was injected intraperitoneally, the learning and memory ability of WT mice were tested by new object recognition, y maze and water maze. The oxidative stress level was detected by the kit. The levels of inflammatory factors were detected by RT-qpcr.
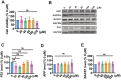
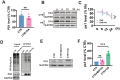
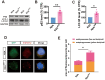
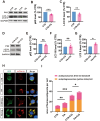
Results: The viability of N2AAPP cells was not affected at different concentrations of PA, but PS1 was significantly decreased at 40μM. PA can obviously improve the accumulation of autophagy in AD, and to some extent save the autophagy inhibition of CQ. Behavioral studies have shown that PA can also improve learning and memory impairments caused by Aβ injections. In addition, in vivo experiments, PA can also improve oxidative stress levels, inflammation levels and salvage dysfunctions of synapses. PA also reduces the levels of total and phosphorylated Tau in N2ATau.
Discussion: Our study provides the first evidence that PA improves learning and memory in Aβ-induced AD mice. This effect appears to be mediated by PA by promoting autophagy and reducing oxidative stress. It was also found that PA may have a role in regulating inflammation, improving abnormally phosphorylated tau, and salvaging damaged synaptic function, providing valuable insights into potential applications in the treatment and prevention of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; PS1; Parishin A; amyloid-β; autophagy.
Copyright © 2025 Guo, Yi, Luo, Dong and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rg1 improves Alzheimer's disease by regulating mitochondrial dynamics mediated by the AMPK/Drp1 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;340:119285. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119285. Epub 2024 Dec 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39733799
-
[Moxibustion improves learning-memory ability by promoting cellular autophagy and regulating autophagy-related proteins in hippocampus and cerebral cortex in APP/PS1 transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Apr 25;44(4):235-41. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180305. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 31056874 Chinese.
-
Shenqi Xingnao Granules ameliorates cognitive impairments and Alzheimer's disease-like pathologies in APP/PS1 mouse model.Chin Herb Med. 2020 Oct 6;12(4):421-429. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2020.04.005. eCollection 2020 Oct. Chin Herb Med. 2020. PMID: 36120170 Free PMC article.
-
Fuzhisan ameliorates cognitive ability in Alzheimer's disease by p62 and related autophagy regulatory pathways.Brain Res. 2025 Feb 15;1849:149436. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2024.149436. Epub 2024 Dec 28. Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39736370
-
Amyloid Beta and Phosphorylated Tau-Induced Defective Autophagy and Mitophagy in Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2019 May 22;8(5):488. doi: 10.3390/cells8050488. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31121890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burt T. D., Agan B. K., Marconi V. C., He W., Kulkarni H., Mold J. E., et al. . (2008). Apolipoprotein (apo) E4 enhances HIV-1 cell entry in vitro, and the APOE ε4/ε4 genotype accelerates HIV disease progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 8718–8723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803526105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

