Explainable machine learning model and nomogram for predicting the efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treating Long COVID: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40182854
- PMCID: PMC11966431
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1529993
Explainable machine learning model and nomogram for predicting the efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treating Long COVID: a retrospective study
Abstract
Introduction: Long COVID significantly affects patients' quality of life, yet no standardized treatment has been established. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) presents a promising potential approach with targeted therapeutic strategies. This study aims to develop an explainable machine learning (ML) model and nomogram to identify Long COVID patients who may benefit from TCM, enhancing clinical decision-making.
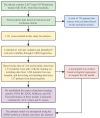
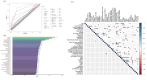
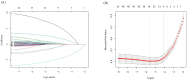
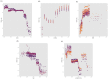
Methods: We analyzed data from 1,331 Long COVID patients treated with TCM between December 2022 and February 2024 at three hospitals in Zhejiang, China. Effectiveness was defined as improvement in two or more symptoms or a minimum 2-point increase in the Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Score (TCMSS). Data included 11 patient and disease characteristics, 18 clinical symptoms and syndrome scores, and 12 auxiliary examination indicators. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method identified features linked to TCM efficacy. Data from 1,204 patients served as the training set, while 127 patients formed the testing set.
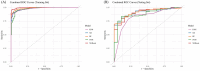
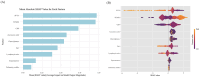
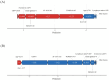
Results: We employed five ML algorithms: Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and Neural Network (NN). The XGBoost model achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.9957 and an F1 score of 0.9852 in the training set, demonstrating superior performance in the testing set with an AUC of 0.9059 and F1 score of 0.9027. Key features identified through SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) included chest tightness, aversion to cold, age, TCMSS, Short Form (36) Health Survey (SF-36), C-reactive protein (CRP), and lymphocyte ratio. The logistic regression-based nomogram demonstrated an AUC of 0.9479 and F1 score of 0.9384 in the testing set.
Conclusion: This study utilized multicenter data and multiple ML algorithms to create a ML model for predicting TCM efficacy in Long COVID treatment. Furthermore, a logistic regression-based nomogram was developed to assist the model and improve decision-making efficiency in TCM applications for Long COVID management.
Keywords: Long COVID; SHapley Additive exPlanations; Traditional Chinese Medicine; efficacy; machine learning; nomogram.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, Zhang, Yang, Ma, Meng, Wu, Zhu, Zhang, Lin and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

