Current Principles in the Management of a Mangled Hand
- PMID: 40182866
- PMCID: PMC11963006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2024.07.009
Current Principles in the Management of a Mangled Hand
Abstract
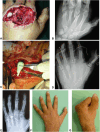
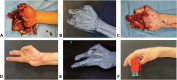
Mangled upper-extremity injuries can have devastating consequences for the patient. The goal of treatment was to recreate a functional hand with a minimum of three sensitive and opposable fingers to achieve an acceptable quality of life. Early management of injuries is critical to treatment success. Initial assessment begins in the emergency department where the injury is quantified and the amputated segments are evaluated, particularly the possibility of replanting them or using them as spare parts as tissue bank. In the operating room, careful debridement is essential for any reconstruction. Despite advances in reconstructive techniques, the management of these injuries is a challenge for the surgeon. The main treatment guidelines and a step-by-step approach to the mangled hand are presented to achieve acceptable results.
Keywords: Mangled hand; Reconstructive microsurgery; Replantation; Revascularization.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received related directly to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early management of the mangled upper extremity.Injury. 2007 Dec;38 Suppl 5:S3-7. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2007.10.038. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Injury. 2007. PMID: 18061189
-
Mangled upper extremity: Our strategy of reconstruction and clinical results.Injury. 2021 Dec;52(12):3588-3604. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2021.04.004. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Injury. 2021. PMID: 33867148
-
"Damage Control" Hand Surgery: Evaluation and Emergency Management of the Mangled Hand.Hand Clin. 2018 Feb;34(1):17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2017.09.002. Hand Clin. 2018. PMID: 29169593 Review.
-
Use of "spare parts" in mutilated upper extremity injuries.Hand Clin. 2003 Feb;19(1):73-87, vi. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0712(02)00143-9. Hand Clin. 2003. PMID: 12683448 Review.
-
Current management of the mangled upper extremity.Int Orthop. 2012 Nov;36(11):2189-95. doi: 10.1007/s00264-012-1638-y. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Int Orthop. 2012. PMID: 22923227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sabapathy S.R., Del Piñal F., Boyer M.I., Lee D.C., Sebastin S.J., Venkatramani H. Management of a mutilated hand: the current trends. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2022;47(1):98–104. - PubMed
-
- Neumeister M.W., Brown R.E. Mutilating hand injuries: principles and management. Hand Clin. 2003;19(1):1–15, v. - PubMed
-
- del Piñal F. Severe mutilating injuries to the hand: guidelines for organizing the chaos. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60(7):816–827. - PubMed
-
- Baltzer H.L., Moran S.L. The biomechanical impact of digital loss and fusion following trauma: setting the patient up for success. Hand Clin. 2016;32(4):443–463. - PubMed
-
- Rich N.M., Baugh J.H., Hughes C.W. Acute arterial injuries in Vietnam: 1,000 cases. J Trauma. 1970;10:359–369. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

