The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture combined with medication in the treatment of perimenopausal insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40183009
- PMCID: PMC11966447
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1476719
The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture combined with medication in the treatment of perimenopausal insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of the combination therapy of acupuncture and medication in the treatment of perimenopausal insomnia (PMI). This research seeks to provide scientific evidence for clinical practice, optimize treatment protocols, and enhance the sleep quality and overall quality of life for women experiencing perimenopausal insomnia.
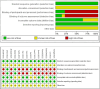
Methods and analysis: A comprehensive search was conducted across 8 databases, including the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Academic Journal Full-text Database (Wanfang), Chongqing VIP Database (CQVIP), China Biology Medicine Disc (CBM), PubMed, Web of Science, Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), and Cochrane Library, from their establishment to July 1, 2024. Outcome measures were analyzed using Review Manager 5.4 and Stata 15.0 software. The included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involved 1,187 patients with perimenopausal sleep disorders (596 in the experimental group and 591 in the control group). The analysis indicated that compared to Western medication alone, the combination therapy showed better efficacy [risk ratio (RR) = 1.24, 95% confidence interval (CI) (1.17, 1.31), p < 0.00001] and safety [RR = 0.31, 95%CI (0.18, 0.53), p < 0.0001]. It also demonstrated more significant improvements in Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) [mean difference (MD) = -2.77, 95%CI (-4.11, -1.43), p < 0.0001], Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAMA) scores [MD = -3.45, 95%CI (-3.94, -2.97), p < 0.00001], Kupperman Menopausal Index (KMI) [MD = -1.46, 95%CI (-2.23, -0.70), p = 0.0002], Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndromes (TCMS) scores [MD = -2.45, 95%CI (-3.85, -1.04), p = 0.0006], and hormone levels, including Luteinizing Hormone (LH) [MD = -4.17, 95%CI (-7.42, -0.93), p = 0.01], Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) [MD = -10.50, 95%CI (-14.80, -6.20), p < 0.00001], and Estradiol (E2) [MD = 12.15, 95%CI (6.79, 17.51), p < 0.00001].
Discussion: The combination therapy demonstrates great efficacy and safety for PMI patients, representing an innovative integrative alternative treatment with high clinical application value.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024564357, PROSPERO CRD42024564357.
Keywords: acupuncture; combination therapy; insomnia; medication; menopause; meta-analysis; perimenopause; systematic review.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


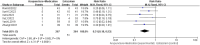




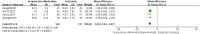
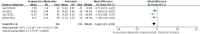

Similar articles
-
Integrated acupuncture-pharmacotherapy for perimenopausal insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Aug 20;16:1633794. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1633794. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40909006 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Xiangshao granules on clinical symptoms and serum hormone levels of menopausal syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 28;16:1546200. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1546200. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40093746 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture combined with Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of perimenopausal insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 10;102(45):e35942. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035942. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37960761 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acupoint application therapy combined with chinese herbal medicine on perimenopausal syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails.Complement Ther Med. 2023 Mar;72:102916. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2023.102916. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Complement Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 36623609
-
Efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation for post-stroke sleep disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1420363. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1420363. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39539650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harlow SD, Gass M, Hall JE, Lobo R, Maki P, Rebar RW, et al. . STRAW+ 10 collaborative group. Executive summary of the stages of reproductive aging workshop+ 10: addressing the unfinished agenda of staging reproductive aging. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:1159–68. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-3362, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

