Targeting gut microbiota: a potential therapeutic approach for tumor microenvironment in glioma
- PMID: 40183013
- PMCID: PMC11965986
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1549465
Targeting gut microbiota: a potential therapeutic approach for tumor microenvironment in glioma
Abstract
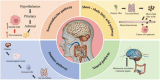
Glioma, being one of the malignant tumors with the highest mortality rate globally, has an unclear pathogenesis, and the existing treatment effects still have certain limitations. The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays an important role in the occurrence, development, and recurrence of glioma. As one of the important regulatory factors of TME, the gut microbiota can regulate the progression of glioma not only by interacting with the brain through the brain-gut axis but also by influencing the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and inflammatory microenvironment. Recent studies have identified the gut microbiota and TME as potential therapeutic targets for glioma. This paper aims to summarize the role of the gut microbiota in TME, the association between them and glioma, and the potential of developing new intervention measures by targeting the gut microbiota. Understanding the involvement process of the gut microbiota in glioma may pave the way for the development of effective treatment methods that can regulate TME and prevent disease progression.
Keywords: dysbiosis; glioma; gut microbiota; microbiota-brain-gut axis; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 Qi, Meng, Zhao, Lv, Huang, Fan and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials