The urinary bladder wall is remodeled by undulatory resistance training in female Wistar rats
- PMID: 40183045
- PMCID: PMC11967418
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19172
The urinary bladder wall is remodeled by undulatory resistance training in female Wistar rats
Abstract
Urinary stress incontinence has a high prevalence in women, with many associated risk factors, such as high impact and intensity sports due to increased intra-abdominal pressure causing stretching and weakening of the pelvic floor muscles. No previous study has investigated the effects of undulatory resistance training (URT), deemed as high impact sports's modality, on urinary bladder (UB) and tissue remodeling. Healing of tissue depends on the equilibrium of metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPS). We aimed to investigate the histomorphological effects of URT on UB wall. Twelve female Wistar rats were randomly divided in two groups: sedentary (SED, n = 5) and URT (n = 7). URT was performed with a ladder climbing equipment after the maximum loaded carrying test (MLCT) was carried out. The training sessions were organized in three blocks increasing the MLCT's weight each block. New MLCT were set at the end of each block. The day after the last training, the rat was euthanized and the UB was harvested and stored in formalin for later histological analysis stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE), Masson's trichrome (MT), picrosirius-hematoxylin (PH) and resorcin-fuchsin (RF), and immunohistochemistry for metalloproteinase-1 (MMP1) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP1). UB slices of URT rats stained with HE showed changes in all UB layers, with increased thickeness of the urothelium. MT staining allowed to observe an increased collagen concentration on the lamina propria layer (LP) of URT rats. PH staining demonstrated a higher luminous intensity for collagen type I and III in lamina propria and smooth muscle layers of the UB wall in the URT group than in SED. RF staining demonstrated an increase of elastic fiber concentration on the LP and smooth muscle layer of the bladder wall in the URT group. Immunohistochemistry of UB slices showed that MMP1 and TIMP1 were immunolabeled on the LP the UB wall in URT rats, with TIMP1 showing a lighter labeling than MMP1. Therefore, the findings suggest that URT induces remodeling of the urinary bladder wall characterized by imbalance between MMP1 and TIMP1 and evoking an alteration in the connective tissue from loose to dense.
Keywords: Collagen; Elastin; Metalloproteinase; Picrosirius; Resorcin; TIMP; Undulatory resistance training; Urinary bladder.
© 2025 Braverman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




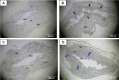
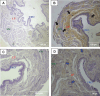
References
-
- Ahmadizad S, Ghorbani S, Ghasemikaram M, Bahmanzadeh M. Effects of short-term nonperiodized, linear periodized and daily undulating periodized resistance training on plasma adiponectin, leptin and insulin resistance. Clinical Biochemistry. 2014;47(6):417–422. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.12.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amerman EC. Human anatomy & physiology. Second Edition. London: Pearson; 2018.
-
- Baker SC, Suthgate J. Electrospinning for Tissue Regeneration. Sawston: Woodhead Publishing; 2011. Bladder tissue regeneration.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

