The interaction between a leflunomide-response methylation site (cg17330251) and variant (rs705379) on response to leflunomide in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40183079
- PMCID: PMC11965123
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1499723
The interaction between a leflunomide-response methylation site (cg17330251) and variant (rs705379) on response to leflunomide in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: This research aims to reveal the mechanisms of the effect of the Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) gene on response to leflunomide (LEF) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, in terms of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), DNA methylation levels.
Methods: A total of 240 RA patients enrolled were categorized into the good response group and the non-response group according to the difference in DAS28 scores between baseline and 6 months after LEF administration. The identified LEF-response cytosine-phosphate-guanines (CpGs) island (cg17330251) and its internal SNPs (rs705379, etc.) located at the PON1 promoter were detected by Sanger sequencing and methyl target sequencing.
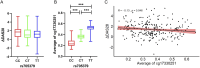
Results: A total of 12 CpG sites at cg17330251 could be identified in our RA patients. There were significant difference between the responders and non-responders in nine CpG sites: cg17330251_2, cg17330251_3, cg17330251_4, cg17330251_6, cg17330251_7, cg17330251_8, cg17330251_9, cg17330251_10, cg17330251_12, [OR (95CI%) = 0.492 (0.250, 0.969), 0.478 (0.243, 0.940), 0.492 (0.250, 0.969), 0.461 (0.234, 0.907), 0.492 (0.250, 0.969), 0.437 (0.225, 0.849), 0.478 (0.243, 0.941), 0.421 (0.212, 0.836), 0.424 (0.213, 0.843), P < 0.05, respectively]. At all these nine CpG sites, the proportions of low methylation levels in the responders were higher than those in the non-responders (P < 0.05). In a dominant model, there was a significant difference in rs705379 wildtype CC and mutant genotypes (CT + TT) between the responders and non-responders (P < 0.05). The average methylation level of 12 CpG sites was lowest in rs705379-CC (median 0.229, IQR 0.195-0.287), then rs705379-CT (median 0.363, IQR 0.332-0.395), and rs705379-TT (median:0.531, IQR:0.496-0.557). The average methylation levels of 12 CpG sites were significantly negative correlated with ΔDAS28 (r = -0.13, P < 0.05). The Logistic regression indicated that combined effect of rs705379, DNA methylation of the PON1 gene [OR (95CI%) = 1.277 [1.003, 1.626)], systemic inflammation index (SIRI) [OR (95CI%) = 1.079 (1.018, 1.143)] served as protective factors on response to LEF in RA patients.
Conclusion: The RA patients with SNP-rs705379-CC, the low methylation level of PON1-cg17330251 and more SIRI would be susceptible of response to LEF and more suitable to choose LEF treatment.
Keywords: DNA methylation4; PON1; leflunomide; rheumatoid arthritis; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Chen, Liu, Jin, Feng, Dai, Chen, Wang, Yao, Liao, Zhao, Qu, Song and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aletaha D., Neogi T., Silman A. J., Funovits J., Felson D. T., Bingham C. O., 3rd, et al. (2010). 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 62(9):2569–2581. 10.1002/art.27584 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

