MEPED as salvage therapy for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma incorporating edited non-oncogene addiction: mTOR as a bottleneck
- PMID: 40183103
- PMCID: PMC11965665
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1553331
MEPED as salvage therapy for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma incorporating edited non-oncogene addiction: mTOR as a bottleneck
Abstract
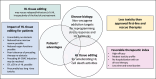
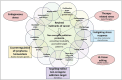
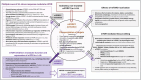
Rescue therapies of relapsed/refractory (r/r) Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) in the third to sixth-line provide major, yet unresolved problems. The MEPED regimen includes nuclear receptor agonists such as pioglitazone and dexamethasone, which counterbalance HL homeostasis, HL stress response inhibitors, everolimus and COX-2 inhibitor, and a stress response inducer, low-dose metronomic treosulfan. CR (six of seven patients) and long-term cCR in patients receiving no consolidating allogeneic stem cell transplantation highlight MEPED as a potent salvage therapy in advanced refractory HL. MEPED edits everolimus activities in such a way that mTORC1 becomes a non-oncogene addiction bottleneck, hence determining long-term therapy outcome. The implications of the therapeutic paradigm shift toward editing of HL tissue, and particularly mTOR addiction, could prove to be profound for clinical practice, both in terms of outcome and treatment tolerability. The long-term results of MEPED treatment indicate the urgent evaluation of the schedule in a multicenter trial for r/r HL.
Keywords: Hodgkin’s lymphoma tissue editing; M-CRAC; anakoinosis; dexamethasone; mTOR; non-oncogene addiction; pioglitazone; relapsed/refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Copyright © 2025 Harrer, Lüke, Pukrop, Ghibelli, Reichle and Heudobler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

