Alveolar macrophages: guardians of the alveolar lipid galaxy
- PMID: 40183504
- PMCID: PMC12043416
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000987
Alveolar macrophages: guardians of the alveolar lipid galaxy
Abstract
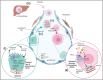
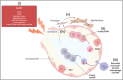
Purpose of review: As the primary guardians at the air-surface interface, the functional profile of alveolar macrophages (AM) is wide-ranging from establishment of the alveolar niche, homeostatic maintenance of surfactant levels, to pathogen clearance and resolution and repair processes. Alveolar lipid homeostasis is disturbed in chronic lung diseases and contributes to disease pathogenesis through extracellular localization in the alveolar lumen or intracellular accumulation in AM. This review aims to provide a focused overview of the state of knowledge of AM, their ontogeny and development during health and disease, and how dysregulated AM lipids play a key role in disease processes, from initiation to resolution.
Recent findings: While lipid-laden macrophages are observed across a broad spectrum of lung diseases, their occurrence has largely been considered consequential. Recent advances in lipidomic profiling of single cell types has revealed that disturbances to lipid homeostasis occur early in disease in tissue-resident cells. Comparisons between inflammatory and fibrotic injury models reveal specific alveolar macrophage subsets with different lipid utilization that contribute to the disease process.
Summary: Understanding the intricate web of AM population seeding and development and how this niche is perturbed by lipid disturbances may help provide leverage for new interventions.
Keywords: alveolar macrophage; cholesterol; lipid; lung disease.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alveolar lipids in pulmonary disease. A review.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jun 3;19(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01278-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32493486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Air Space Distension Precedes Spontaneous Fibrotic Remodeling and Impaired Cholesterol Metabolism in the Absence of Surfactant Protein C.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020 Apr;62(4):466-478. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0358OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31922895
-
Lung surfactant metabolism: early in life, early in disease and target in cell therapy.Cell Tissue Res. 2017 Mar;367(3):721-735. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2520-9. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Cell Tissue Res. 2017. PMID: 27783217 Review.
-
Pharmacological activation of liver X receptor during cigarette smoke exposure adversely affects alveolar macrophages and pulmonary surfactant homeostasis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 Apr 1;316(4):L669-L678. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00482.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30702343
-
Temsirolimus induces surfactant lipid accumulation and lung inflammation in mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Jun 15;306(12):L1117-28. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00251.2013. Epub 2014 May 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24793166
References
-
- Goerke J. Pulmonary surfactant: functions and molecular composition. Biochim Biophys acta 1998; 1408:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Tarling E. Expanding roles of ABCG1 and sterol transport. Curr Opin Lipidol 2013; 24:138–146. - PubMed
-
- Tarling EJ, Edwards PA. Dancing with the sterols: critical roles for ABCG1, ABCA1, miRNAs, and nuclear and cell surface receptors in controlling cellular sterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1821:386–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

