Real-world avelumab first-line maintenance in advanced urothelial carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40184226
- PMCID: PMC11988210
- DOI: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2475734
Real-world avelumab first-line maintenance in advanced urothelial carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: This systematic literature review summarizes the real-world effectiveness, safety, and tolerability of avelumab first-line maintenance (1LM) in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (la/mUC).
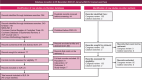
Materials & methods: Database searches (MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane) and manual gray literature searches of real-world studies published from 01/01/2020-31/01/2024 were performed. Pooled 12-month overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) rates were synthesized by meta-analysis.
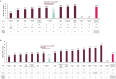
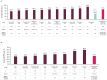
Results: Across 45 unique studies including >2,600 patients, median OS and PFS were 21.3 and 7.0 months, respectively. In the meta-analysis, 12-month OS and PFS rates (95% CI) from avelumab 1LM start were 69% (65-73%) and 39% (35-44%), respectively.
Conclusion: This study supports the established clinical benefit of avelumab 1LM across a broad range of patients with la/mUC in routine practice.
Keywords: Real-world evidence; avelumab; first-line maintenance; locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma; systematic literature review.
Plain language summary
Bladder cancer is called advanced when it has spread outside of the urinary tract. People with advanced bladder cancer can be treated with chemotherapy followed by maintenance treatment with a drug called avelumab if their cancer has not gotten worse (i.e. not progressed) after chemotherapy. Maintenance treatment is given to people to slow down or stop the growth of the cancer. In this study, the researchers looked at real‑world evidence in people with advanced bladder cancer who received avelumab maintenance after chemotherapy. Real‑world evidence refers to information about a disease or drug that is gathered outside of clinical trials. Real-world evidence allows researchers to assess whether the outcomes and side effects of treatments seen in controlled clinical trials are similar in routine clinical practice. The researchers conducted a review of published real-world evidence and found 45 studies that included more than 2,600 people with advanced bladder cancer who were treated with avelumab maintenance after chemotherapy. The researchers found that people who received avelumab maintenance in real-world studies experienced similar benefits to people who received avelumab maintenance in clinical trials, including survival benefits, slower cancer progression, and comparable side effects. These results could increase confidence in using avelumab maintenance treatment following chemotherapy among doctors, decision-makers, researchers, and people with advanced bladder cancer and their caregivers, despite the availability of newer treatments. More real-world evidence is needed to investigate the most effective treatments for people with advanced bladder cancer.
Figures


References
-
- European Association of Urology . Muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. Guidelines Available from: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/muscle-invasive-and-metastatic-bladder-can...
-
- Powles T, Bellmunt J, Comperat E, et al. ESMO clinical practice guideline interim update on first-line therapy in advanced urothelial carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2024;35(6):485–490. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.03.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
• The updated guidelines from the European Society of Medical Oncology provide recommendations for the treatment of la/mUC, including avelumab 1LM in patients with no progression after 1L chemotherapy as an alternative to enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab or nivolumab, gemcitabine, and cisplatin.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
