Isoquercitrin Alleviates Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting STAT3 Phosphorylation and Dimerization
- PMID: 40184310
- PMCID: PMC12224983
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202414587
Isoquercitrin Alleviates Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting STAT3 Phosphorylation and Dimerization
Abstract
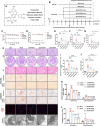
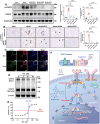
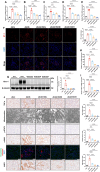
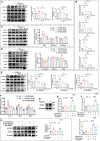
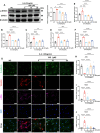
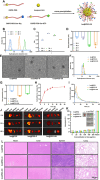
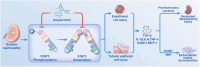
At the convergence point of multiple cytokine signals, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a highly promising therapeutic target for diabetic nephropathy. Isoquercitrin, a natural small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3, may have beneficial effects on diabetic nephropathy; however, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Isoquercitrin significantly mitigated renal inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting STAT3 activity in mice with diabetic nephropathy. Moreover, STAT3 is a direct molecular target of isoquercitrin, which as corroborated by tight and stable noncovalent binding between them. This interaction is mechanistically supported by the affinity of isoquercitrin for the Ser668-Gln635-Gln633 region within the pY+1 binding pocket of the SH2 domain. This binding obstructs pivotal processes like STAT3 phosphorylation and dimerization, thereby suppressing its transcriptional function. Finally, a kidney-targeted nanocarrier, Iso@PEG-GK, is developed to load isoquercitrin, thus enhancing its therapeutic precision for diabetic nephropathy. Iso@PEG-GK significantly improved the absorption and renal distribution of isoquercitrin. This study is the first to demonstrate that isoquercitrin exerts a significant protective effect against diabetic nephropathy and may provide a novel therapeutic drug for this disease.
Keywords: Iso@PEG‐GK; SH2 domain; STAT3; diabetic nephropathy; dimerization; isoquercitrin; phosphorylation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
