Tirzepatide Versus Semaglutide on Weight Loss in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Direct Comparative Studies
- PMID: 40184508
- PMCID: PMC11970626
- DOI: 10.1002/edm2.70045
Tirzepatide Versus Semaglutide on Weight Loss in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Direct Comparative Studies
Abstract
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have emerged as an efficacious treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and have demonstrated substantial weight loss effects. This systematic review compares two prevalent GLP-1RAs, tirzepatide and semaglutide, with their weight loss effects and rates of adverse events (AEs).
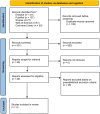
Methods: Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), a systematic search was performed in PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library for direct comparative studies between tirzepatide and semaglutide. A meta-analysis was conducted via a random-effects model to analyse the differences in weight loss outcomes between study cohorts.
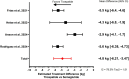
Results: Four studies, with 28,827 patients (14,870 tirzepatide/13,928 semaglutide), mean age of 55.7 years (52.0 to 63.7) and mean follow-up of 35.9 weeks (23.6 to 44.6), were included in this study. Mean weight change across four studies for tirzepatide and semaglutide was -11.4% (-15.3% to -8.27%) and -7.3% (-8.3% to -6.08%), respectively. The meta-analysis supports these findings with a mean difference of -4.84 kg (95% CI: -6.21 to -3.47), favouring tirzepatide. The most common AEs were minor and moderate-severity gastrointestinal (GI) AEs.
Conclusion: Current literature supports tirzepatide demonstrating a higher impact on weight loss than semaglutide, with both demonstrating high rates of minimal- to moderate-severity AEs. Further research with comparative head-to-head trials will better elucidate these weight loss effects and safety profiles.
Keywords: diabetes; meta‐analysis; semaglutide; tirzepatide; weight loss.
© 2025 The Author(s). Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Panuganti K. K., Nguyen M., and Kshirsagar R. K., “Obesity,” in StatPearls (StatPearls Publishing, 2024).
-
- Latif W., Lambrinos K. J., Patel P., and Rodriguez R., “Compare and Contrast the Glucagon‐Like Peptide‐1 Receptor Agonists (GLP1RAs),” in StatPearls (StatPearls Publishing, 2024).
-
- Collins L. and Costello R. A., “Glucagon‐Like Peptide‐1 Receptor Agonists,” in StatPearls (StatPearls Publishing, 2024).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical