Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing With Forehead and Popliteal Oximetry in Evaluating Efficacy of Reverse Potts Shunt
- PMID: 40185583
- PMCID: PMC12046823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2025.103409
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing With Forehead and Popliteal Oximetry in Evaluating Efficacy of Reverse Potts Shunt
Abstract
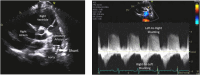
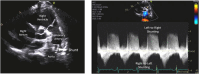
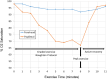
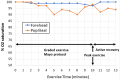
Reverse Potts shunt (rPS) is a surgical procedure that creates an anastomosis between the left pulmonary artery and descending aorta to decompress the right ventricle in suprasystemic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). In this paper, we introduce a unique procedure combining cardiopulmonary exercise testing with forehead and popliteal oximetry to evaluate the efficacy of the rPS. Our study involved tests on 4 patients with PAH who had the shunt in place. We found that the level of oxygen saturation in the popliteal artery decreased during exercise and correlated with the rPS efficacy and the overall clinical outcome. In conclusion, we demonstrate a simple, noninvasive technique for evaluating patency and function of rPS in patients with suprasystemic PAH.
Keywords: CPET; NYHA; PAH; VO(2) max; forehead saturation; oxygen saturation; popliteal saturation; pulmonary hypertension; reverse Potts shunt; right to left shunt.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kaminsky L.A., Arena R., Myers J., et al. Updated reference standards for cardiorespiratory fitness measured with cardiopulmonary exercise testing: data from the fitness registry and the Importance of Exercise National Database (FRIEND) Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97(2):285–293. - PubMed
-
- Daida H., Allison T.G., Johnson B.D., Squires R.W., Gau G.T. Comparison of peak exercise oxygen uptake in men versus women in chronic heart failure secondary to ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1997;80(1):85–88. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

