Epidermal electronic-tattoo for plant immune response monitoring
- PMID: 40185801
- PMCID: PMC11971386
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58584-x
Epidermal electronic-tattoo for plant immune response monitoring
Abstract
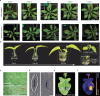
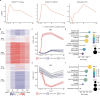
Real-time monitoring of plant immune responses is crucial for understanding plant immunity and mitigating economic losses from pathogen and pest attacks. However, current methods relying on molecular-level assessment are destructive and time-consuming. Here, we report an ultrathin, substrate-free, and highly conductive electronic tattoo (e-tattoo) designed for plants, enabling immune response monitoring through non-invasive electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The e-tattoo's biocompatibility, high conductivity, and sub-100 nm thickness allow it to conform to leaf tissue morphology and provide robust impedance data. We demonstrate continuous EIS analysis of live transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants for over 24 h, capturing the onset of NLR-mediated acute immune responses within three hours post-induction, prior to visible symptoms. RNA-seq and tissue ion leakage tests validate that EIS data accurately represent the physiological and molecular changes associated with immune activation. This non-invasive tissue-assessment technology has the potential to enhance our comprehension of immune activation mechanisms in plants and paves the way for real-time monitoring for plant health management.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interaction of the Arabidopsis GTPase RabA4c with its effector PMR4 results in complete penetration resistance to powdery mildew.Plant Cell. 2014 Jul;26(7):3185-200. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.127779. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25056861 Free PMC article.
-
The pathogen-induced peptide CEP14 is perceived by the receptor-like kinase CEPR2 to promote systemic disease resistance in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2024 Dec 23;197(1):kiae549. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae549. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39412292
-
Generating Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants for Functional Analysis of Pathogen Effectors and Corresponding R Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1991:199-206. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9458-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31041774
-
Arabidopsis CURLY LEAF functions in leaf immunity against fungal pathogens by concomitantly repressing SEPALLATA3 and activating ORA59.Plant J. 2021 Nov;108(4):1005-1019. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15488. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 34506685
-
NPR1 in JazzSet with Pathogen Effectors.Trends Plant Sci. 2018 Jun;23(6):469-472. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 May 9. Trends Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29753632 Review.
References
-
- Pathogens, precipitation and produce prices. Nat. Clim. Change11, 635–635 (2021).
-
- Savary, S. et al. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol3, 430–439 (2019). - PubMed
-
- McDowell, J. M. & Dangl, J. L. Signal transduction in the plant immune response. Trends Biochem. Sci.25, 79–82 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Laflamme, B., Middleton, M., Lo, T., Desveaux, D. & Guttman, D. S. Image-based quantification of plant immunity and disease. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact.29, 919–924 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

