Genomics and multiomics in the age of precision medicine
- PMID: 40185865
- PMCID: PMC12106083
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-025-04021-0
Genomics and multiomics in the age of precision medicine
Abstract
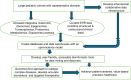
Precision medicine is a transformative healthcare model that utilizes an understanding of a person's genome, environment, lifestyle, and interplay to deliver customized healthcare. Precision medicine has the potential to improve the health and productivity of the population, enhance patient trust and satisfaction in healthcare, and accrue health cost-benefits both at an individual and population level. Through faster and cost-effective genomics data, next-generation sequencing has provided us the impetus to understand the nuances of complex interactions between genes, diet, and lifestyle that are heterogeneous across the population. The emergence of multiomics technologies, including transcriptomics, proteomics, epigenomics, metabolomics, and microbiomics, has enhanced the knowledge necessary for maximizing the applicability of genomics data for better health outcomes. Integrative multiomics, the combination of multiple 'omics' data layered over each other, including the interconnections and interactions between them, helps us understand human health and disease better than any of them separately. Integration of these multiomics data is possible today with the phenomenal advancements in bioinformatics, data sciences, and artificial intelligence. Our review presents a broad perspective on the utility and feasibility of a genomics-first approach layered with other omics data, offering a practical model for adopting an integrated multiomics approach in pediatric health care and research. IMPACT: Precision medicine provides a paradigm shift from a conventional, reactive disease control approach to proactive disease prevention and health preservation. Phenomenal advancements in bioinformatics, data sciences, and artificial intelligence have made integrative multiomics feasible and help us understand human health and disease better than any of them separately. The genotype-first approach or reverse phenotyping has the potential to overcome the limitations of the phenotype-first approach by identifying new genotype-phenotype associations, enhancing the subclassification of diseases by widening the phenotypic spectrum of genetic variants, and understanding functional mechanisms of genetic variations.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

