Streamlined gram-scale natural N-glycan production using reversible tagging after oxidative release of natural glycans
- PMID: 40185879
- PMCID: PMC11971423
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-025-01499-x
Streamlined gram-scale natural N-glycan production using reversible tagging after oxidative release of natural glycans
Abstract
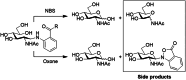
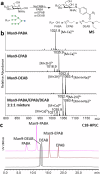
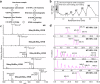
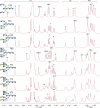
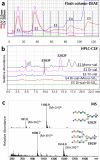
The study of natural glycans is fundamental to modern glycomics; however, the functional analysis of these glycans is limited by their low natural abundance, structural heterogeneity, and the absence of efficient preparative-scale isolation methods. Here, we present a streamlined approach for the gram-scale production of complex natural N-glycans in their reducing form by combining oxidative release of natural glycans (ORNG) using household bleach, an innovative cleavable tag chemistry, and optimized multi-dimensional chromatography. Our ORNG process releases N-glycans from kilogram-scale of natural sources containing various glycoproteins, which can be efficiently attached with a 4-aminobenzoate tag, facilitating the selective separation of these glycans from other biomolecules. The tagged glycans can be purified via dry-load HILIC flash chromatography at gram scale followed by reverse-phase HPLC. Treatment with Oxone quantitatively cleaves the tag, regenerating the free reducing N-glycans in high yield. This method provides an accessible, gram-scale source of complex N-glycans, including complex asymmetric structures that are challenging to synthesize through conventional chemoenzymatic approaches. We believe this approach represents a versatile strategy for acquiring complex natural glycans, opening new avenues for the functional exploration of N-glycans in glycoscience.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): X.S. is co-founder and consultant of NatGlycan LLC, which is commercializing the ORNG technology. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Large scale preparation of high mannose and paucimannose N-glycans from soybean proteins by oxidative release of natural glycans (ORNG).Carbohydr Res. 2018 Jul 15;464:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 15. Carbohydr Res. 2018. PMID: 29803109 Free PMC article.
-
O-Benzylhydroxylamine (BHA) as a Cleavable Tag for Isolation and Purification of Reducing Glycans.SLAS Technol. 2020 Aug;25(4):388-396. doi: 10.1177/2472630319898150. Epub 2020 Jan 21. SLAS Technol. 2020. PMID: 31959063
-
Oxidative Release of Natural Glycans: Unraveling the Mechanism for Rapid N-Glycan Glycomics Analysis.Anal Chem. 2024 Oct 22;96(42):16750-16757. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c03246. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39387489 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Complex Glycans From Natural Sources for Functional Study.Front Chem. 2020 Jul 3;8:508. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00508. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32719769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Applications of chromatography in glycomics].Se Pu. 2024 Jul;42(7):646-657. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.12003. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38966973 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Jaeken, J. & Matthijs, G. Congenital disorders of glycosylation. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet.2, 129–151 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Mrksich, M. An early taste of functional glycomics. Chem. Biol.11, 739–740 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Ohtsubo, K. & Marth, J. D. Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell126, 855–867 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Shriver, Z., Raguram, S. & Sasisekharan, R. Glycomics: a pathway to a class of new and improved therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.3, 863–873 (2004). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

