An eRNA transcription checkpoint for diverse signal-dependent enhancer activation programs
- PMID: 40186057
- PMCID: PMC12286646
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02138-w
An eRNA transcription checkpoint for diverse signal-dependent enhancer activation programs
Abstract
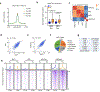
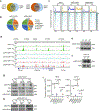
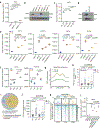
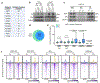
The evidence that signal- and ligand-dependent pathways function by activating regulatory enhancer programs suggests that a 'checkpoint' strategy may underline activation of many diversely regulated enhancers. Here we report a molecular mechanism common to several acute signal- and ligand-dependent enhancer activation programs based on release of a shared enhancer RNA (eRNA) transcription checkpoint. It requires recruitment of a DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs)-phosphorylated RING finger repressor (Krüppel-associated box)-associated protein 1 (KAP1) as a modulator, inhibiting its association with 7SK and E3 small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) ligase activity on the CDK9 subunit of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb). This facilitates formation of an activated P-TEFb complex, licensing eRNA elongation. Overcoming this checkpoint for signal-dependent enhancer activation occurs in diverse pathways, including estrogen receptor-α, NF-κB-regulated proinflammatory stimulation, androgen receptor and neuronal depolarization. Therefore, a specific strategy required to convert a basal state enhancer P-TEFb complex to an active state to release a conserved checkpoint is apparently employed by several functionally important signal-regulated regulatory enhancers to implement the instructions of the endocrine and paracrine system.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

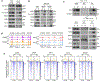
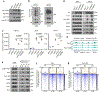
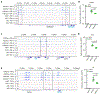

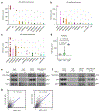

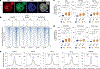
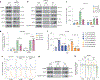



References
-
- Banerji J et al. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell 27, 299–308 (1981). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG074307/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK007541/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01AG070154/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R01 AG067556/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35-GM131780/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070154/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK039949/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R35 GM131780/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

