Deep learning model for detecting cystoid fluid collections on optical coherence tomography in X-linked retinoschisis patients
- PMID: 40186400
- PMCID: PMC12340181
- DOI: 10.1111/aos.17495
Deep learning model for detecting cystoid fluid collections on optical coherence tomography in X-linked retinoschisis patients
Abstract
Purpose: To validate a deep learning (DL) framework for detecting and quantifying cystoid fluid collections (CFC) on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) in X-linked retinoschisis (XLRS) patients.
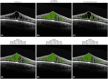
Methods: A no-new-U-Net model was trained using 112 OCT volumes from the RETOUCH challenge (70 for training and 42 for internal testing). External validation involved 37 SD-OCT scans from 20 XLRS patients, including 20 randomly sampled B-scans and 17 manually selected central B-scans. Three graders manually delineated the CFC on these B-scans in this external test set. The model's efficacy was evaluated using Dice and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) scores, assessed exclusively on the test set comprising B-scans from XLRS patients.
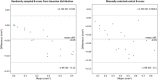
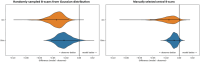
Results: For the randomly sampled B-scans, the model achieved a mean Dice score of 0.886 (±0.010), compared to 0.912 (±0.014) for the observers. For the manually selected central B-scans, the Dice scores were 0.936 (±0.012) for the model and 0.946 (±0.012) for the graders. ICC scores between the model and reference were 0.945 (±0.014) for the randomly selected and 0.964 (±0.011) for the manually selected B-scans. Among the graders, ICC scores were 0.979 (±0.008) and 0.981 (±0.011), respectively.
Conclusions: Our validated DL model accurately segments and quantifies CFC on SD-OCT in XLRS, paving the way for reliable monitoring of structural changes. However, systematic overestimation by the DL model was observed, highlighting a key limitation for future refinement.
Keywords: AI in ophthalmology; X‐linked juvenile retinoschisis; cystoid macular oedema; deep learning; deep reinforcement learning; image segmentation; optical coherence tomography.
© 2025 The Author(s). Acta Ophthalmologica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Figures

References
-
- Apushkin, M.A. & Fishman, G.A. (2006) Use of dorzolamide for patients with X‐linked retinoschisis. Retina, 26, 741–745. - PubMed
-
- Bogunovic, H. , Venhuizen, F. , Klimscha, S. , Apostolopoulos, S. , Bab‐Hadiashar, A. , Bagci, U. et al. (2019) RETOUCH: the retinal OCT fluid detection and segmentation benchmark and challenge. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 38(8), 1858–1874. Available from: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2901398 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cukras, C. , Wiley, H.E. , Jeffrey, B.G. , Sen, H.N. , Turriff, A. , Zeng, Y. et al. (2018) Retinal AAV8‐RS1 gene therapy for X‐linked retinoschisis: initial findings from a phase I/IIa trial by intravitreal delivery. Molecular Therapy, 26(9), 2282–2294. Available from: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.05.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

