CellEKT: A Robust Chemical Proteomics Workflow to Profile Cellular Target Engagement of Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 40187492
- PMCID: PMC12172290
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100961
CellEKT: A Robust Chemical Proteomics Workflow to Profile Cellular Target Engagement of Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
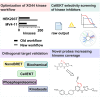
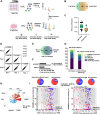
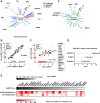
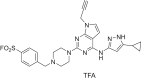
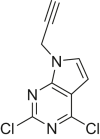
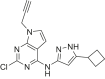
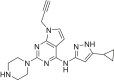
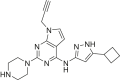
The human genome encodes 518 protein kinases that are pivotal for drug discovery in various therapeutic areas, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders. The majority of kinase inhibitors target the conserved ATP-binding pocket, making it difficult to develop selective inhibitors. To characterize and prioritize kinase-inhibiting drug candidates, efficient methods are desired to determine target engagement (TE) across the cellular kinome. In this study, we present CellEKT (Cellular Endogenous Kinase Targeting), an optimized and robust chemical proteomics platform for investigating cellular TE of endogenously expressed kinases using the sulfonyl fluoride-based probe XO44 and two new probes ALX005 and ALX011. The optimized workflow enabled the determination of the kinome interaction landscape of covalent and noncovalent drugs across over 300 kinases, expressed as IC50, which were validated using distinct platforms like phosphoproteomics and NanoBRET. With CellEKT, TE profiles were linked to their substrate space. CellEKT has the ability to decrypt drug actions and to guide the discovery and development of drugs.
Keywords: CellEKT; activity-based protein profiling; broad-spectrum kinase probes; cellular target engagement; chemical proteomics; endogenous kinome profiling.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest A. V., R. H., H. W., P. W., A. T., B. W., S. K., J. D. Z., U. G., and A. C. R. are employees of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. J. R., B. G. and M. v. d. S. are financially supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Chemical probes ALX005 and ALX011 are filed as patent with J. R. and M. v. d. S. listed as inventors.
Figures






References
-
- Manning G., Whyte D.B., Martinez R., Hunter T., Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson F.M., Gray N.S. Kinase inhibitors: the road ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018;17:353–377. - PubMed
-
- Roskoski R. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: a 2024 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2024;200 - PubMed
-
- Davis M.I., Hunt J.P., Herrgard S., Ciceri P., Wodicka L.M., Pallares G., et al. Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011;29:1046–1051. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

