Inhibition of Interleukin-8/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor 2 Signaling Axis Prevents Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 40188812
- PMCID: PMC12105825
- DOI: 10.1159/000545659
Inhibition of Interleukin-8/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor 2 Signaling Axis Prevents Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
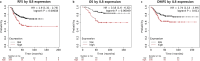
Introduction: Previously, we reported that interleukin-8 (IL-8) was associated with poor prognosis of basal-like breast cancer patients and has been identified as a pro-tumorigenic factor, facilitating cell invasion and migration. Here, we investigated the pharmacological impact of inhibitors targeting the chemokine receptors, C-X-C chemokine receptor 1 (CXCR1) and C-X-C chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2), which are activated by IL-8.
Methods: The survival rates of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients by IL-8 were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier plotter. The levels of mRNA and protein expression were analyzed by real-time PCR and Western blotting. The alteration of apoptotic cell death-related proteins by SB225002 was analyzed by the Proteome Profiler Human Apoptosis Array. Cell growth was analyzed by MTT and colony-forming assay. Apoptosis and cell cycle were analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting.
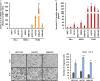
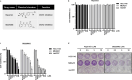
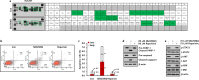
Results: Aberrant IL-8 expression is involved with the prognosis of TNBC patients. Basal IL-8 levels are markedly elevated in TNBC cells compared to those in HER2+ and/or ER+ breast cancer cells. Furthermore, recombinant human IL-8 treatment enhanced cell invasiveness in TNBC cells. To counteract the tumor-promoting effects of IL-8, we assessed the therapeutic potential of CXCR1 and CXCR2 inhibitors. Notably, while reparixin, a CXCR1-specific inhibitor, exhibited no impact on cell viability, SB225002, a CXCR2-specific inhibitor, significantly reduced cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. There was a noticeable reduction in the levels of anti-apoptotic biomarkers, including Bcl-2, cIAP-1, cIAP-2, Survivin, XIAP, HIF-1α, and HO-1, following SB225002 treatment. Our findings indicate an increase in the apoptotic cell population with SB225002 treatment in TNBC cells. In xenograft models, SB225002 effectively diminished the metastatic potential of 4T1 cells, which are known to metastasize to the lung and liver.
Conclusion: Our results underscore the significant role of the IL-8/CXCR2 signaling axis in the metastasis of TNBC and suggest that CXCR2 inhibitors such as SB225002 may be promising therapeutic agents for TNBC patients.
Keywords: Apoptosis; C-X-C chemokine receptor 1; C-X-C chemokine receptor 2; Interleukin-8; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ononin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer lung metastasis by targeting the EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Sep;67(9):1849-1866. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2499-2. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38900236
-
Zhuidu Formula suppresses the migratory and invasive properties of triple-negative breast cancer cells via dual signaling pathways of RhoA/ROCK and CDC42/MRCK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Oct 28;315:116644. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116644. Epub 2023 May 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37196814
-
Astragaloside IV inhibits the growth of obesity-associated triple-negative breast cancer by activating FOXA1 transcription factor to regulate GAL3ST1-GalCer signaling and remodel sphingolipid metabolism.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156907. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156907. Epub 2025 May 29. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40472617
-
An update on cancer stem cell survival pathways involved in chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Mar;21(6):715-735. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2461443. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39936282 Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
Cited by
-
G protein-coupled receptors: pivotal hubs in gastric cancer malignancy-from multidimensional crosstalk to precision therapeutics.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 7;23(1):879. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06851-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40775711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CXCL1-CXCR2 Axis as a Component of Therapy Resistance, a Source of Side Effects in Cancer Treatment, and a Therapeutic Target.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 15;17(10):1674. doi: 10.3390/cancers17101674. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12–49. - PubMed
-
- de Gramont A, Watson S, Ellis LM, Rodón J, Tabernero J, de Gramont A, et al. Pragmatic issues in biomarker evaluation for targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(4):197–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

