KAP1 promotes gastric adenocarcinoma progression by activating Hippo/YAP1 signaling via binding to HNRNPAB
- PMID: 40189014
- PMCID: PMC12165730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217695
KAP1 promotes gastric adenocarcinoma progression by activating Hippo/YAP1 signaling via binding to HNRNPAB
Abstract
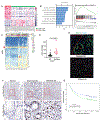
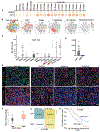
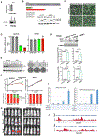
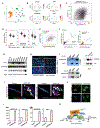
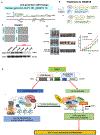
Gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC) remains a significant global health challenge, with over a million new cases annually. Peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC), detected in ∼20 % of cases at diagnosis and ∼45 % later, is uniformly fatal, with limited treatment options. This study investigated the role of KAP1 in GAC progression, focusing on its interaction with YAP1 and cancer stemness traits. Analysis of over 596 primary GACs and 72 PC samples revealed that high nuclear KAP1 expression correlates with poor prognosis. KAP1 knockdown reduced oncogenic activity and stemness traits in GAC cells. Mechanistically, KAP1 positively regulates YAP1 transcription by binding to its promoter and reducing H3K27ac levels. Mass spectrometry identified an interaction between KAP1 and HNRNPAB, further modulating YAP1 signaling. Expression of the KRAB domain of ZFP568 without its DNA-binding zinc fingers inhibited both KAP1 and YAP1 expression, significantly reducing colony formation and tumor growth in vivo. Additionally, emerging antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) targeting KAP1 or YAP1 effectively suppressed mouse tumor progression. These findings establish KAP1 as a critical driver of tumor progression in GAC through YAP1 regulation and HNRNPAB interaction, highlighting its potential therapeutic target. This study advances our understanding and offers a preclinical framework to improve outcomes for GAC.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotides; CDH1; H3K27ac; Patient derived ascites; Single cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Salati M, Orsi G, Smyth E, Aprile G, Beretta G, De Vita F, Di Bartolomeo M, Fanotto V, Lonardi S, Morano F, Pietrantonio F, Pinto C, Rimassa L, Vasile E, Vivaldi C, Zaniboni A, Ziranu P, Cascinu S, Gastric cancer: translating novels concepts into clinical practice, Cancer Treat Rev. 79 (2019) 101889. - PubMed
-
- Lei T, Lin Y, Lai X, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Wang X, Liu W, Tang Q, Yang T, Feng W, Song W, ITGB5 facilitates gastric cancer metastasis by promoting TGFBR2 endosomal recycling, Cancer Lett. 592 (2024) 216953. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Fu L, Wang H, Yonemura A, Semba T, Yasuda-Yoshihara N, Nishimura A, Tajiri T, Tong Y, Yasuda T, Uchihara T, Yamazaki M, Okamoto Y, Yamasaki J, Nagano O, Baba H, Ishimoto T, RAC1-mediated integrin alpha-6 expression in E-cadherin-deficient gastric cancer cells promotes interactions with the stroma and peritoneal dissemination, Cancer Lett. 591 (2024) 216901. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

