Good long-term results of sacral neuromodulation for endometriosis related chronic pelvic pain
- PMID: 40189530
- PMCID: PMC11974166
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-025-03699-y
Good long-term results of sacral neuromodulation for endometriosis related chronic pelvic pain
Abstract
Background: Sacral neuromodulation (SNM) is an established therapy in urology and gastroenterological surgery for treatment of overactive bladder symptoms, urge urinary incontinence or fecal incontinence. SNM has also been used with good results in patients with chronic pelvic pain (CPP). Our aim was to analyze long-term results of SNM in Finnish patients with endometriosis related CPP.
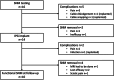
Methods: This is a register-based retrospective study including all the endometriosis patients treated with SNM for CPP in Finland between 2004 and 2017. There were four centers where these procedures were performed, two University Hospitals and two Central Hospitals. Long-term results were assessed by phone interview in spring 2021.
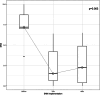
Results: A total of 16 women with endometriosis, with a median age of 39 (25-50) years, underwent SNM treatment for chronic pelvic pain (CPP), with the median follow-up time of 73 (48-85) months. The Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG) was implanted to 14 patients (88%). By the end of the follow-up period, 10 patients (62,5% of all patients and 71% of those who received IPG) had a functional SNM. Pain was assessed by numeral rating scale (NRS) and decreased from a median of 7.4 (3.6-10) to 2.3 (0-6.5).
Conclusions: SNM could be a good option in the treatment of endometriosis related chronic pelvic pain when standard therapy is not enough.
Keywords: Chronic pelvic pain; Endometriosis; Sacral neuromodulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with Finnish Medical Research Act 488/199, 295/2004 and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital District of Southwest Finland (ETMK: 163/1801/2015, ETMK 7/2019). Informed consent to participate was obtained from all of the participants in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- StatPearls. 2021.
-
- Mahran A, Baaklini G, Hassani D, Abolella HA, Safwat AS, Neudecker M et al. Sacral neuromodulation treating chronic pelvic pain: a meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature. Int Urogynecol J. 2019. Epub 2019/03/16. 10.1007/s00192-019-03898-w. PubMed PMID: 30874835. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical