Developing a standardized framework for evaluating health apps using natural language processing
- PMID: 40189623
- PMCID: PMC11973176
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96369-w
Developing a standardized framework for evaluating health apps using natural language processing
Abstract
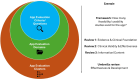
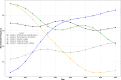
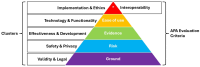
Despite regulatory efforts, many smartphone health applications remain unregulated, raising concerns about privacy, security, and evidence-based effectiveness. The lack of standardized regulation has led to the proliferation of over 130 frameworks, introducing new criteria and methodologies for app evaluation. The sheer number of frameworks, coupled with their varying approaches to app evaluation, create challenges for comparison. Our study aims to synthesize existing knowledge and propose a standardized app evaluation framework. We conducted a synthesis of reviews on health app evaluation frameworks. Using natural language processing (NLP), we analyzed evaluation domains and grouped them into clusters based on semantic similarities. Standardized definitions for these clusters were developed. We identified eight review articles that met the inclusion criteria, each proposing between six and 17 app evaluation domains. Using NLP, we identified five clusters of app evaluation: Effectiveness & Development, Technology & Functionality, Validity & Legal, Safety & Privacy, and Implementation & Ethics, each of which was assigned a standardized definition. The clusters align with but expand on the American Psychiatric Association's evaluation domains, incorporating critical aspects such as inclusivity, safety, engagement, and ethical principles. Temporal analysis revealed an increasing focus on Effectiveness & Development, while Safety & Privacy showed a stagnation in attention over time.
Keywords: App evaluation framework; Information management; Mobile health apps; Natural Language processing; Telemedicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Google How google play works (2024). https://play.google/howplayworks/ (2024).
-
- Apple, A. App Store. https://www.apple.com/app-store/ (2024).
-
- Bates, D. W., Landman, A. & Levine, D. M. Health Apps and Health Policy: What Is Needed? JAMA320, 1975 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Business of Apps. Health App Revenue and Usage Statistics. (2024). https://www.businessofapps.com/data/health-app-market/?utm_source=chatgp...
-
- Serpwatch App Usage Statistics 2024: Downloads, Revenue, Popularity. https://serpwatch.io/blog/app-usage-statistics/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

