The impact of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on colorectal cancer development and prevention
- PMID: 40189834
- PMCID: PMC11980463
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2483780
The impact of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on colorectal cancer development and prevention
Abstract
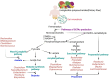
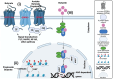
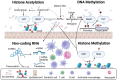
Cancer is a long-term illness that involves an imbalance in cellular and immune functions. It can be caused by a range of factors, including exposure to environmental carcinogens, poor diet, infections, and genetic alterations. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for overall health, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced by gut microbiota play a vital role in this process. Recent research has established that alterations in the gut microbiome led to decreased production of SCFA's in lumen of the colon, which associated with changes in the intestinal epithelial barrier function, and immunity, are closely linked to colorectal cancer (CRC) development and its progression. SCFAs influence cancer progression by modifying epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA functions thereby affecting tumor initiation and metastasis. This suggests that restoring SCFA levels in colon through microbiota modulation could serve as an innovative strategy for CRC prevention and treatment. This review highlights the critical relationship between gut microbiota and CRC, emphasizing the potential of targeting SCFAs to enhance gut health and reduce CRC risk.
Keywords: CRC prevention; Short chain fatty acids; gut microbiome; immune modulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Jean Wilson E, Sirpu Natesh N, Ghadermazi P, Pothuraju R, Prajapati DR, Pandey S, Kaifi JT, Dodam JR, Bryan JN, Lorson CL, et al. Red cabbage juice-mediated gut microbiota modulation improves intestinal epithelial homeostasis and ameliorates colitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;25(1):539. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010539. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
