Association between human herpesviruses and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a molecular perspective
- PMID: 40189853
- PMCID: PMC11973434
- DOI: 10.5144/0256-4947.2025.104
Association between human herpesviruses and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a molecular perspective
Abstract
Background: Head and neck cancer (HNC) is the seventh most common malignant tumor. Herpesviruses are a significant risk factor in the multifactorial pathogenesis of HNC.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the association between herpesviruses and the development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HN-SCC).
Design: Experimental study.
Setting: A university hospital in Turkey.
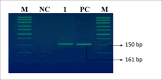
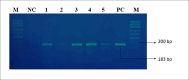
Patients and methods: Pathological archive tissue samples of 500 patients were included in the study. These samples were categorized into two groups: those diagnosed with HN-SCC (n=300, malignant group [MG]) and those diagnosed with benign head and neck lesions (n=200, benign group [BG]). The presence of herpesvirus in samples was detected using polymerase chain reaction.
Main outcome measures: Association of herpesviruses in the development of head and neck cancer.
Sample size: 500 patients.
Results: HHV-1, -2, -7, and -8 were not detected in any samples. In the malignant group (MG), EBV-DNA was detected in 1 patient (0.3%) and HHV-6 DNA in 2 patients (0.6%), while in the benign group (BG), VZV-DNA was detected in 1 patient (0.5%), EBV-DNA in 3 patients (1.5%), CMV-DNA in 5 patients (2.5%), and HHV-6 DNA in 3 patients (1.5%). While no significant difference was found between the groups for VZV, EBV, and HHV-6, a statistically significant difference was found in favor of the benign group for CMV.
Conclusion: Although herpesvirus seroprevalence is relatively high in the population, the lack of viral genome in tissue samples indicates that other factors might be prominent in developing HN-SCC.
Limitation: The storage conditions of the sample used (paraffinized sample) may have negatively affected the detection frequency of HHVs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Carlander A-LF, Larsen CG, Jensen DH, Garnæs E, Kiss K, Andersen L, et al.. Continuing rise in oropharyngeal cancer in a high HPV prevalence area: A Danish population-based study from 2011 to 2014. European Journal of Cancer. 2017;70:75–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

