The role of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity in development and disease
- PMID: 40191103
- PMCID: PMC11968406
- DOI: 10.1038/s44341-025-00014-6
The role of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity in development and disease
Abstract
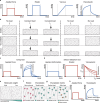
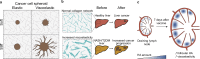
For several decades, research has studied the influence of the extracellular matrix (ECM) mechanical properties in cell response, primarily emphasising its elasticity as the main determinant of cell and tissue behaviour. However, the ECM is not purely elastic; it is viscoelastic. ECM viscoelasticity has now emerged as a major regulator of collective cell dynamics. This review highlights recent findings on the role of ECM viscoelasticity in development and pathology.
Keywords: Biological physics; Biophysics; Biotechnology; Cell biology; Diseases; Physics.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The extracellular matrix viscoelasticity as a regulator of cell and tissue dynamics.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021 Oct;72:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2021.04.002. Epub 2021 May 13. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33993058 Review.
-
Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour.Nature. 2020 Aug;584(7822):535-546. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2612-2. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32848221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viscoelasticity of ECM and cells-origin, measurement and correlation.Mechanobiol Med. 2024 Jul 31;2(4):100082. doi: 10.1016/j.mbm.2024.100082. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mechanobiol Med. 2024. PMID: 40395221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viscoelastic Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022 Jul;28(7):289-300. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2022.0040. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022. PMID: 35442107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viscoelastic Mechanics: From Pathology and Cell Fate to Tissue Regeneration Biomaterial Development.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Feb 12;17(6):8751-8770. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c18174. Epub 2025 Feb 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 39899815 Review.
Cited by
-
Micro-computed tomography to visualize preserved vascular architecture in decellularized human vaginal tissue: explorative study.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 20;15(1):30533. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14452-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40835856 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanobiology in Action: Biomaterials, Devices, and the Cellular Machinery of Force Sensing.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 10;15(6):848. doi: 10.3390/biom15060848. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomechanics of the tumor extracellular matrix and regulatory T cells: regulatory mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Aug 21;23(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02380-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40842015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel Network Architecture Design Space: Impact on Mechanical and Viscoelastic Properties.Gels. 2025 Jul 30;11(8):588. doi: 10.3390/gels11080588. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40868719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
