The role of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity in development and disease
- PMID: 40191103
- PMCID: PMC11968406
- DOI: 10.1038/s44341-025-00014-6
The role of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity in development and disease
Abstract
For several decades, research has studied the influence of the extracellular matrix (ECM) mechanical properties in cell response, primarily emphasising its elasticity as the main determinant of cell and tissue behaviour. However, the ECM is not purely elastic; it is viscoelastic. ECM viscoelasticity has now emerged as a major regulator of collective cell dynamics. This review highlights recent findings on the role of ECM viscoelasticity in development and pathology.
Keywords: Biological physics; Biophysics; Biotechnology; Cell biology; Diseases; Physics.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
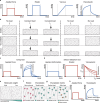

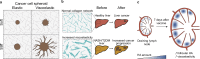
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
