Discovery of a New Class of Thiazolidin-4-one-Based Inhibitors of Human Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase: Biological Activity Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics
- PMID: 40191330
- PMCID: PMC11966315
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11459
Discovery of a New Class of Thiazolidin-4-one-Based Inhibitors of Human Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase: Biological Activity Evaluation, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
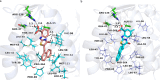
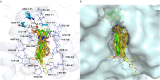
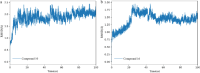
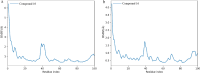
The continuous outbreak of various viruses reminds us to prepare broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (hDHODH) inhibitor exhibits broad-spectrum antiviral effects. In order to explore the novel type of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor (hDHODHi), we have optimized, designed, and synthesized 17 compounds and conducted biological activity evaluation, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics studies. The results of biological activity evaluation showed that compounds 10 and 16 exhibited submicromolar inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 0.188 ± 0.004 and 0.593 ± 0.012 μM, respectively. Molecular docking studies showed that compounds 10 and 16 were in good agreement with the hDHODH activity pocket and interacted well with amino acid residues. Compared to the cocrystallized structure of the brequinar analogue complex, inhibitors 10 and 16 increased their direct interaction with Ala55. In addition, molecular dynamics studies showed that inhibitors 10 and 16 have strong affinity for proteins, and their complexes are stable, which confirms the significant inhibitory effect of inhibitors 10 and 16 on hDHODH in vitro. Through analysis, it was found that the carboxyl group and para introduced fluorine atoms in R 1, as well as the naphthalene in R 2, are key factors in improving activity. This conclusion provides help for further research into hDHODH inhibitors in the future. This study has promoted the significance of the development of broad-spectrum antiviral drugs.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery a series of novel inhibitors of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase: Biological activity evaluation and molecular docking.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024 Jan;103(1):e14388. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14388. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37926553
-
Tiratricol, a thyroid hormone metabolite, has potent inhibitory activity against human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023 Jul;102(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14256. Epub 2023 Apr 23. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023. PMID: 37088711
-
Synthesis of 2-,4,-6-, and/or 7-substituted quinoline derivatives as human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (hDHODH) inhibitors and anticancer agents: 3D QSAR-assisted design.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Apr 1;29(7):917-922. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.01.038. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 30738663
-
Recent advances of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors for cancer therapy: Current development and future perspectives.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Mar 15;232:114176. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114176. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35151222 Review.
-
Use of human Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (hDHODH) Inhibitors in Autoimmune Diseases and New Perspectives in Cancer Therapy.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018;13(1):86-105. doi: 10.2174/1574892812666171108124218. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29119937 Review.
References
-
- WHO , H1N1 IHR Emergency Committee, 2009. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/h1n1-ihr-emergency-committee.
-
- WHO , Poliovirus IHR Emergency Committee, 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/poliovirus-ihr-emergencycommittee.
-
- WHO , Ebola Virus Disease in West Africa (2014–2015) IHR Emergency Committee, 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/ebola-virus-disease-in-west-africa-(2014-2015....
-
- WHO , Zika Virus IHR Emergency Committee, 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/zika-virus-ihr-emergencycommittee.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
