Solvent-Induced Chirality Switching in the Enantioseparation of Hydroxycarboxylic Acids with a Quaternary Stereogenic Center
- PMID: 40191346
- PMCID: PMC11966323
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10205
Solvent-Induced Chirality Switching in the Enantioseparation of Hydroxycarboxylic Acids with a Quaternary Stereogenic Center
Abstract
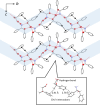
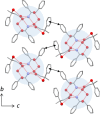
The enantiomer separation of three isomeric hydroxycarboxylic acids with a quaternary stereogenic center via diastereomeric salt formation with (1R,2S)-2-amino-1,2-diphenylethanol was demonstrated. Racemic acid 1, with a quaternary chiral center at the β-position, was separated with nearly ideal efficiency. The stereochemistry of acids 2 and 3 incorporated in the less-soluble salts was reversed depending on the recrystallization solvents, and both enantiomers were accessible. The mechanism of this chirality switching was discussed based on the crystal structures of the less-soluble diastereomeric salts; the solvation of the salt with an alcohol molecule changed the hydrogen-bonding network and its stability.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kozma D.CRC Handbook of Optical Resolutions via Diastereomeric Salt Formation; CRC Press, 2001.
-
- Kodama K.; Shitara H.; Hirose T. Chirality Switching in Optical Resolution of Mandelic Acid in C1–C4 Alcohols: Elucidation of Solvent Effects Based on X-ray Crystal Structures of Diastereomeric Salts. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14 (7), 3549–3556. 10.1021/cg500483p. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
