A cross-sectional study on the effects of bedtime administration of selective α1 adrenoceptor antagonists on nocturnal blood pressure in elderly patients with benign prostate hyperplasia
- PMID: 40191753
- PMCID: PMC11970415
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19165
A cross-sectional study on the effects of bedtime administration of selective α1 adrenoceptor antagonists on nocturnal blood pressure in elderly patients with benign prostate hyperplasia
Abstract
Background: It remains uncertain whether a bedtime dose of selective α1 adrenoceptor antagonist could result in nocturnal hypotension in elderly patients with benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH).
Methods: A total of 253 older men with BPH who had taken selective α1 adrenoceptor antagonists before sleep were consecutively recruited from the Geriatric Department of Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital. A total of 221 patients were finally included in the analysis with qualified data including office blood pressure examinations, biochemical tests of blood, and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Nocturnal hypotension was defined according to the nighttime average systolic blood pressure of ambulatory blood pressure ≤ 100 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≤ 60 mmHg. Explore the presence of night hypotension, compare the characteristics of the two groups with or without nocturnal hypotension, and analyze the related risk factors.
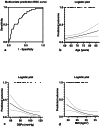
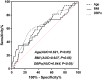
Results: Among all 221 patients included in the analysis, nocturnal hypotension occurred in 38 patients (17.2%). Compared with those without, patients with nocturnal hypotension were older, had less body mass index, lower office diastolic blood pressure, and lower ambulatory blood pressure in a 24 hour day, and night systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and were less likely to have hypertension. Age (OR 1.064, 95% CI [1.012-1.118], P = 0.015) and no hypertension (OR 2.548, 95% CI [1.211-5.359], P = 0.014) were independently associated with the presence of nocturnal hypotension.
Discussion: Nocturnal hypotension was common in men 60 years and older with BPH treated with selective α1 adrenoceptor antagonists before sleep. Age and no hypertension were independently associated with nocturnal hypotension positively. Related factors may help clinicians identify hypotension tendencies in the elderly when prescribing such drugs.
Keywords: Adrenergic alpha-1 receptor antagonist; Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; Geriatric medicine; Nocturnal hypotension; The elderly.
©2025 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
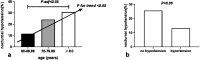
Similar articles
-
A double-blind comparison of terazosin and tamsulosin on their differential effects on ambulatory blood pressure and nocturnal orthostatic stress testing.Eur Urol. 1998;33(5):481-8. doi: 10.1159/000019639. Eur Urol. 1998. PMID: 9643668 Clinical Trial.
-
Initiation of nonselective alpha1-antagonist therapy and occurrence of hypotension-related adverse events among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a retrospective cohort study.Clin Ther. 2001 May;23(5):727-43. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80022-9. Clin Ther. 2001. PMID: 11394731
-
Treatment-time regimen of hypertension medications significantly affects ambulatory blood pressure and clinical characteristics of patients with resistant hypertension.Chronobiol Int. 2013 Mar;30(1-2):192-206. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2012.701460. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Chronobiol Int. 2013. PMID: 23098160 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacology of alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists.Eur Urol. 1999;36 Suppl 1:48-53; discussion 65. doi: 10.1159/000052318. Eur Urol. 1999. PMID: 10393473 Review.
-
Adrenoceptor pharmacology: urogenital applications.Eur Urol. 1999;36 Suppl 1:17-22. doi: 10.1159/000052313. Eur Urol. 1999. PMID: 10393468 Review.
References
-
- Albasri A, Hattle M, Koshiaris C, Dunnigan A, Paxton B, Fox SE, Smith M, Archer L, Levis B, Payne RA, Riley RD, Roberts N, Snell KIE, Lay-Flurrie S, Usher-Smith J, Stevens R, Hobbs FDR, McManus RJ, Sheppard JP, STRATIFY investigators Association between antihypertensive treatment and adverse events: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;372:n189. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bird ST, Delaney JA, Brophy JM, Etminan M, Skeldon SC, Hartzema AG. Tamsulosin treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia and risk of severe hypotension in men aged, years in the United States: risk window analyses using between and within patient methodology. BMJ. 2013;347:f6320. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f6320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Divisón-Garrote JA, Banegas JR, Dela Cruz JJ, Escobar-Cervantes C, Dela Sierra A, Gorostidi M, Vinyoles E, Abellán-Aleman J, Segura J, Ruilope LM. Hypotension based on office and ambulatory monitoring blood pressure. Prevalence and clinical profile among a cohort of 70,997 treated hypertensives. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension. 2016;10(9):714–723. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2016.06.035. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

