Inferior alveolar nerve damage related to dental implant placement. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40192114
- PMCID: PMC12221155
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.27125
Inferior alveolar nerve damage related to dental implant placement. A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: A concern associated with implant placement is the potential occurrence of neurovascular lesions and subsequent development of sensory alterations in patients undergoing implant placements. The objective of this review is to evaluate the incidence of neurosensory alterations based on the proximity between the implant and the mandibular canal Material and Methods: A systematic review was conducted in MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Scopus. Studies with common variables were selected to conduct a meta-analysis. The patient classification was based on the mandibular canal-implant distance. Neurosensory alteration percentages were calculated for each study and group.
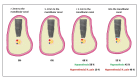
Results: The findings indicate significant correlations between implant placement proximity and neurosensory risks. The incidence of neurosensory alterations in patients with implants placed at a distance ≥ 2 mm from the mandibular canal was 0%. Similarly, for distances between 1-2 mm from the mandibular canal, the incidence remained at 0%. However, for implants placed at a distance of 0-1 mm from the mandibular canal, the incidence of neurosensory alterations was 68%. Additionally, patients with implants that intruded into the canal had an incidence of 53% in the development of neurosensorial alterations.
Conclusions: A distance of 1 mm from the mandibular canal might be safe. Implants placed at a distance less than 1 mm from the mandibular canal exhibit neurosensory alterations. Clinicians should be aware of the potential risk of nerve injury and adopt appropriate precautions, including meticulous preoperative planning and three-dimensional radiographic images.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of sinus lift procedures for dental implant rehabilitation: a Cochrane systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010 Spring;3(1):7-26. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010. PMID: 20467595
-
Soft tissue management for dental implants: what are the most effective techniques? A Cochrane systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012 Autumn;5(3):221-38. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012. PMID: 23000707
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: different types of dental implants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD003815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003815.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 22;(7):CD003815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003815.pub4. PMID: 17943800 Updated.
-
Influence of subcrestal implant placement compared with equicrestal position on the peri-implant hard and soft tissues around platform-switched implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2018 Mar;22(2):555-570. doi: 10.1007/s00784-017-2301-1. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Clin Oral Investig. 2018. PMID: 29313133
-
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: different types of dental implants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jan 25;(1):CD003815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003815.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD003815. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003815.pub3. PMID: 15674915 Updated.
References
-
- Jacobs R, Quirynen M, Bornstein MM. Neurovascular disturbances after implant surgery. Periodontol 2000. 2014;66:188–202. - PubMed
-
- Froum SJ, Bergamini M, Reis N, Wang W, Leung M, Kaufman Z. A New Concept of Safety Distance to Place Implants in the Area of the Inferior Alveolar Canal to Avoid Neurosensory Disturbance. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41:e139–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

