Off-Label Use of Topical Ruxolitinib in Dermatology: A Systematic Literature Review and Current Perspectives
- PMID: 40192197
- PMCID: PMC11974361
- DOI: 10.1111/exd.70095
Off-Label Use of Topical Ruxolitinib in Dermatology: A Systematic Literature Review and Current Perspectives
Abstract
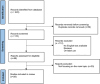
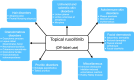
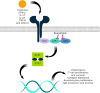
JAK inhibitors are used to treat various inflammatory skin diseases. However, systemic formulations are associated with an increased risk of major adverse events. Ruxolitinib 1.5% cream is a selective topical JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, which has recently been approved by EMA and MHRA for treating non-segmental vitiligo, while being FDA-approved for both vitiligo and atopic dermatitis. Recent literature has reported the off-label use of topical Ruxolitinib for several skin conditions, but data are mostly limited to single case reports and series and few prospective studies, with mixed results. We conducted a systematic review of the literature to investigate the potential efficacy of topical Ruxolitinib in various skin diseases in an off-label setting. The following keywords were used for searching the MEDLINE (Pubmed) and Scopus databases from inception to September 2024: "ruxolitinib cream and dermatology" and "topical ruxolitinib and dermatology". Reviews, articles not focusing on the main topic, books and book chapters, and articles with no English text were excluded. A total of 170 studies were screened, of which 112 fell within exclusion criteria and 58 were assessed for eligibility. Of these, 28 studies, published between 2012 and 2024, were selected. Ruxolitinib cream resulted in being used off-label mostly for treating lichenoid and granulomatous dermatoses, as well as alopecia areata. While for the former skin conditions, topical ruxolitinib proved to be effective and safe, results on efficacy in alopecia areata were controversial. Topical ruxolitinib might be a promising therapeutic option for lichenoid and granulomatous dermatoses. Noteworthily, despite the exciting results from the oral formulation, no consistent data were described for topical ruxolitinib in alopecia areata. Our review reported encouraging results for many inflammatory skin conditions that should be investigated in further studies.
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; dermatology; off‐label; ruxolitinib cream; topical ruxolitinib.
© 2025 The Author(s). Experimental Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Muddebihal A., Khurana A., and Sardana K., “JAK Inhibitors in Dermatology: The Road Travelled and Path Ahead, a Narrative Review,” Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 16 (2023): 279–295. - PubMed
-
- Klein B., Treudler R., and Simon J. C., “JAK‐Inhibitors in Dermatology ‐ Small Molecules, Big Impact? Overview of the Mechanism of Action, Previous Study Results and Potential Adverse Effects,” Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 20 (2022): 19–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous