Pregnancy loss and its predictors among ever-pregnant women in Sub-Saharan Africa: Multilevel mixed effect negative binomial regression
- PMID: 40193521
- PMCID: PMC11975090
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0004316
Pregnancy loss and its predictors among ever-pregnant women in Sub-Saharan Africa: Multilevel mixed effect negative binomial regression
Abstract
Background: Pregnancy loss is a significant maternal health issue in Sub-Saharan Africa. Africa has the highest rates of stillbirths globally, with an estimated 2.7 million stillbirths occurring each year on the continent. The pregnancy loss data are underreported and inconsistently recorded in Sub-Saharan Africa. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the number of pregnancy loss and its predictors among ever-pregnant women in Sub-Saharan Africa using a recent round of demographic and health survey (DHS) data.
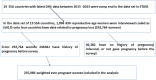
Method: A secondary data analysis was conducted among 235,086 weighted ever-pregnant women in Sub-Saharan Africa using a recent round of DHS data from 2015-2023. Multilevel mixed effect negative binomial regression was conducted. An adjusted incidence rate ratio (AIRR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was reported.
Result: The median number of pregnancy loss in Sub-Saharan Africa is 2.67, 95%CI (2.64, 2.69). A one-year increase in maternal age [AIRR= 1.05, 95%CI (1.06, 1.07)], primary educational status of the mother [AIRR = 1.10, 95% CI (1.01, 1.22)], women with a partner who has higher education [AIRR= 1.18, 95% CI (1.04, 1.39)], a higher number of under-five children [AIRR =0.95, 95% CI (0.91,0.99)], women have ever pregnant in Cote'divore [AIRR 1.76, 95% CI (1.6, 2)] are associated with the number of pregnancy loss.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that there are three pregnancy losses among ever-pregnant women in Sub-Saharan Africa. Notably, a one-year increase in maternal age and higher education levels for both mothers and their partners are linked to an increased risk of pregnancy loss. In contrast, mothers with multiple children generally experience lower rates of loss. Therefore, policy interventions should address the heightened risk of pregnancy loss linked to advancing maternal age and higher education levels for both mothers and their partners. This can be achieved by supporting programs that educate prospective parents about the effects of maternal age on pregnancy outcomes. Furthermore, promoting flexible educational pathways and providing career support can encourage healthier timing for pregnancies. Additionally, initiatives that support families and promote larger family sizes may help reduce pregnancy loss rates in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Copyright: © 2025 Endawkie. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors and number of antenatal care visits among reproductive age women in Sub-Saharan Africa further analysis of recent demographic and health survey from 2017-2023: Zero-inflated negative binomial regression.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 22;19(10):e0302297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302297. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39436932 Free PMC article.
-
Number of antenatal care visits and associated factors among reproductive age women in Sub-Saharan Africa using recent demographic and health survey data from 2008-2019: A multilevel negative binomial regression model.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022 Dec 27;2(12):e0001180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001180. eCollection 2022. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36962803 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary feeding practices and associated factors among mothers of children aged 6 to 23 months in Sub-saharan African countries: a multilevel analysis of the recent demographic and health survey.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 8;24(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-17629-w. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38191351 Free PMC article.
-
Bottle-feeding practice and its associated factors among mothers of children aged 0 to 23 months in sub-Saharan Africa: a multi-level analysis of demographic and health surveys (2015-2022).BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 26;24(1):1712. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19244-9. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38926817 Free PMC article.
-
Minimum milk feeding frequency and its associated factors among non-breastfed children aged 6-23 months in sub-saharan Africa: a multilevel analysis of the recent demographic and health survey data.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 28;24(1):1734. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19275-2. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38943130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D.K. PhD. What is pregnancy loss and why does it matter.
-
- Sarah Prager M, Elizabeth M, Vanessa KD. Pregnancy loss (miscarriage): Clinical presentations, diagnosis, and initial evaluation.” 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources