Completing the BASEL phage collection to unlock hidden diversity for systematic exploration of phage-host interactions
- PMID: 40193529
- PMCID: PMC11990801
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003063
Completing the BASEL phage collection to unlock hidden diversity for systematic exploration of phage-host interactions
Abstract
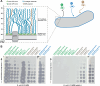
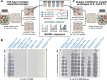
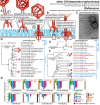
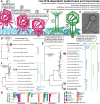
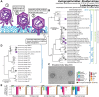
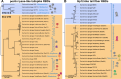
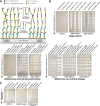
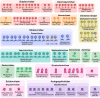
Research on bacteriophages, the viruses infecting bacteria, has fueled the development of modern molecular biology and inspired their therapeutic application to combat bacterial multidrug resistance. However, most work has so far focused on a few model phages which impedes direct applications of these findings in clinics and suggests that a vast potential of powerful molecular biology has remained untapped. We have therefore recently composed the BASEL collection of Escherichia coli phages (BActeriophage SElection for your Laboratory), which made a relevant diversity of phages infecting the E. coli K-12 laboratory strain accessible to the community. These phages are widely used, but their assorted diversity has remained limited by the E. coli K-12 host. We have therefore now genetically overcome the two major limitations of E. coli K-12, its lack of O-antigen glycans and the presence of resident bacterial immunity. Restoring O-antigen expression resulted in the isolation of diverse additional viral groups like Kagunavirus, Nonanavirus, Gordonclarkvirinae, and Gamaleyavirus, while eliminating all known antiviral defenses of E. coli K-12 additionally enabled us to isolate phages of Wifcevirus genus. Even though some of these viral groups appear to be common in nature, no phages from any of them had previously been isolated using E. coli laboratory strains, and they had thus remained largely understudied. Overall, 37 new phage isolates have been added to complete the BASEL collection. These phages were deeply characterized genomically and phenotypically with regard to host receptors, sensitivity to antiviral defense systems, and host range. Our results highlighted dominant roles of the O-antigen barrier for viral host recognition and of restriction-modification systems in bacterial immunity. We anticipate that the completed BASEL collection will propel research on phage-host interactions and their molecular mechanisms, deepening our understanding of viral ecology and fostering innovations in biotechnology and antimicrobial therapy.
Copyright: © 2025 Humolli et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Schaechter M, Kolter R, editors. Small Things Considered [Internet]. 2022. https://schaechter.asmblog.org/schaechter/2022/03/the-phage-treaty.html2022. [cited 2022]. Available from: https://schaechter.asmblog.org/schaechter/2022/03/the-phage-treaty.html
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

