Clinical outcomes of plate-haptic diffractive multifocal toric IOL in cataract eyes with long axial length and corneal astigmatism
- PMID: 40195538
- PMCID: PMC11977217
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97040-0
Clinical outcomes of plate-haptic diffractive multifocal toric IOL in cataract eyes with long axial length and corneal astigmatism
Abstract
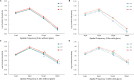
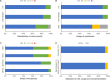
The prospective study is aimed to determine the clinical outcomes of plate-haptic diffractive multifocal toric intraocular lens (IOL) implantation in cataract patients with long axial length and corneal astigmatism. Visual outcomes, defocus curves, contrast sensitivity, rotational stability, vector changes of refractive astigmatism and patient satisfaction were assessed over 3 months. Vector analysis was performed by the Alpins method. A total of 36 eyes (18 patients) underwent cataract surgery with implantation of AT LISA toric 909 M multifocal toric IOL. Preoperatively, mean axial length AL was 27.31 ± 2.20 mm. Mean manifest sphere and cylinder were - 6.66 ± 5.37 diopter (D) and - 1.88 ± 1.11 D. Postoperatively, mean manifest sphere and cylinder were reduced to 0.13 ± 0.23 D and - 0.29 ± 0.32 D, respectively (P < 0.05, Wilcoxon test). Mean uncorrected distance and near visual acuities (logMAR) were 0.40 ± 0.10 and 0.19 ± 0.16, respectively. At 3 months, 91.7% of patients showed IOL rotation of less than 5 degrees. The difference vector was 0.34 ± 0.26 D, for a correction index of 0.93 ± 0.40 at 3 months. In summary, plate-haptic diffractive multifocal toric IOL improves distance and near visual functions and reduces refractive astigmatism in cataract patients with long axial length and corneal astigmatism.Trial registration: NCT04833491.
Keywords: Cataract surgery; Corneal astigmatism; Long axial length; Multifocal toric IOL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Tideman, J. W. et al. Association of axial length with risk of uncorrectable visual impairment for Europeans with myopia. JAMA Ophthalmol.134, 1355–1363. 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2016.4009 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Leske, M. C., Wu, S. Y., Nemesure, B. & Hennis, A. Risk factors for incident nuclear opacities. Ophthalmology109, 1303–1308. 10.1016/s0161-6420(02)01094-1 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Sigireddi, R. R. & Weikert, M. P. How much astigmatism to treat in cataract surgery. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol.31, 10–14. 10.1097/icu.0000000000000627 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- LTGY24H120004/Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation
- 52203191/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 82271042/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2023C03090/Zhejiang Province Key Research and Development Program
- 2020YFE0204400/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

