Automated and Fully Validated High-Throughput LC-MS/MS Assay for Analyzing Multiple Drugs of Abuse in Oral Fluids Using Novel Features in Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Conditions
- PMID: 40195875
- PMCID: PMC11976379
- DOI: 10.1002/jms.5132
Automated and Fully Validated High-Throughput LC-MS/MS Assay for Analyzing Multiple Drugs of Abuse in Oral Fluids Using Novel Features in Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Conditions
Abstract
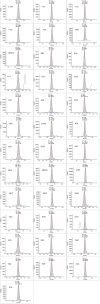
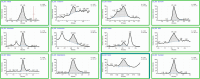
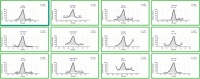
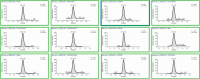
Oral fluid sampling offers advantages over other biological matrices, mainly due to its noninvasive procedure avoiding privacy intrusion. The fully automated sample preparation procedure is based on salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction (SALLE) combined with high-efficiency LC-MS/MS methods for both screening and confirmation of 37 drugs and incorporates novel features enabling direct injection of acetonitrile extracts into an innovative chromatographic system. The methods' drug panel includes opioids, benzodiazepines, benzodiazepine-like drugs, cannabinoids, and stimulants. A full method validation was performed using OF/buffer from Greiner Bio-ONE International and Quantisal saliva collection devices. The validation included assessments of linearity, sensitivity, precision, accuracy, extraction recovery, matrix effects, process efficiency, stability, and carryover. All compounds demonstrated linearity across the concentration range 1-25 ng/mL, with R2 ≥ 0.99. Both methods' limit of detection ranged between 0.001 and 0.03 ng/mL, and the limit of quantification ranged between 0.02 and 0.09 ng/mL. Precision was ≤ 14.8% for screening and ≤ 8.5% for the confirmation method. Accuracy was ± 13.6% for screening and ± 8.7% (except at 0.5 and 1 ng/mL, where it was ± 25.3% and ± 17.6%, respectively) for the confirmation method. Extraction recoveries ranged from 40.0% to 95.1%, except for hydromorphone (27.4%) and morphine (34.4%). Although matrix effects were observed for a large number of compounds to varying degrees, they were largely compensated for by the use of deuterium- and 13C-labeled internal standards (IS). IS-corrected overall process efficiency ranged from 100.7% to 119.1% with precision (CV%) ≤ 10.8% for all compounds. Spiked calibrators and QC samples in OF were stable in autosampler for up to 72 h and in the freezer for 3 days. Methanol working solutions were stable for 6 months. No significant carryover was observed. The methods have been successfully implemented in the routine analysis of approximately > 1000 samples per month since March 2024.
Keywords: Greiner Bio‐One; LC‐MS/MS; Quantisal; SALLE; drugs of abuse; liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; oral fluid; saliva; salting‐out assisted liquid–liquid extraction.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Mass Spectrometry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determination of 21 drugs in oral fluid using fully automated supported liquid extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS.Drug Test Anal. 2017 May;9(5):808-823. doi: 10.1002/dta.2045. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Drug Test Anal. 2017. PMID: 27464485
-
Validation of an LC-MS-MS method for analysis of 58 drugs of abuse in oral fluid and method comparison with an established LC-HRMS method.J Anal Toxicol. 2025 Jan 20;49(1):14-25. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkae087. J Anal Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39492753
-
A broad-spectrum LC-MS/MS method for screening and quantification of 100 analytes in clinical and autopsy blood samples.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2024 Oct 15;1247:124323. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2024.124323. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39306869
-
A fully validated LC-QTOF-MS screening workflow for the analysis of drugs in oral fluid.J Anal Toxicol. 2025 Apr 12;49(4):265-271. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkaf013. J Anal Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39964060
-
Interpretation of oral fluid tests for drugs of abuse.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Mar;1098:51-103. doi: 10.1196/annals.1384.037. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17332074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

