This is a preprint.
Opportunities and challenges of integrating digital health into medical education curricula: A scoping review
- PMID: 40195979
- PMCID: PMC11975014
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6254999/v1
Opportunities and challenges of integrating digital health into medical education curricula: A scoping review
Abstract
Background: The global strategy for digital health advocates digital health literacy in formal education and training curricula for all health professionals. However, little is known about the opportunities and challenges of integrating digital health into medical training curricula.
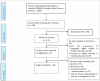
Methods: Guided by Arksey and O'Malley's scoping review methodology, we searched the PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect scholarly databases for peer-reviewed articles published between 2014 and 2024. Data extraction was guided by the consolidated framework for implementation research.
Results: Thirty studies met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed. The opportunities identified include the need for healthcare digitalization, reshaping the future daily work of healthcare professionals, decreasing students' doubts about digital health and increasing the quality of patients' care. On the other hand, a lack of infrastructure and educational materials, the dense nature of the existing curriculum, and bureaucratic tendencies were identified as challenges. The provision of consolidated funds and the establishment of dedicated digital health infrastructure, starting with elective and audited modular approaches, raising awareness, and educating stakeholders, emerged as implementation strategies for mitigating these challenges.
Conclusion: Global progress toward integrating digital health literacy in formal medical training curricula remains slow. There is a need for concerted efforts and political commitment to offer guidance and moral and financial support for this integration.
Keywords: challenges; digital health; integration; medical curricula; opportunities.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- ALFALLAJ H. A., AFRASHTEHFAR K. I., ASIRI A. K., ALMASOUD F. S., ALNAQA G. H. & AL-ANGARI N. S. 2022. The status of digital dental technology implementation in the Saudi dental schools’ curriculum: a national cross-sectional survey for healthcare digitization. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20, 321. - PMC - PubMed
-
- ARKSEY H. & O’MALLEY L. 2005. Scoping studies: toward a methodological framework. International journal of social research methodology, 8, 19.
-
- ASSEMBLY, G. 2015. Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 11 September 2015. New York: United Nations.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous