This is a preprint.
ACTG A5409 (RAD-TB): Study Protocol for a Phase 2 Randomized, Adaptive, Dose-Ranging, Open-Label Trial of Novel Regimens for the Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- PMID: 40195983
- PMCID: PMC11975035
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5931694/v1
ACTG A5409 (RAD-TB): Study Protocol for a Phase 2 Randomized, Adaptive, Dose-Ranging, Open-Label Trial of Novel Regimens for the Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Update in
-
ACTG A5409 (RAD-TB): Study protocol for a phase 2 randomized, adaptive, dose-ranging, open-label trial of novel regimens for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis.Trials. 2025 Aug 15;26(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s13063-025-08973-w. Trials. 2025. PMID: 40817073 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The standard of care (SOC) treatment for drug-susceptible pulmonary tuberculosis (DS-TB) consists of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol (HRZE). New treatment regimen options for DS-TB are needed as HRZE is long in duration (6 months), associated with frequent adverse events, unforgiving of adherence lapses, and complicated by rifamycin-based drug-drug interactions. The recent resurgence of TB drug development, particularly in the context of drug-resistant TB, offers promise for additional regimens for persons with DS-TB, provided they are sufficiently effective and well-tolerated. We spotlight wave 1 of the RAD-TB platform trial (ACTG A5409, NCT06192160) that will investigate new chemical entities for the treatment of DS-TB.
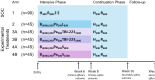
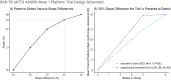
Methods: In wave 1 of the RAD-TB platform, adult participants initiating treatment for DS-TB will be randomized to SOC (HRZE, Arm 1) or one of five experimental arms for the 8-week intensive phase. The experimental treatment arms will consist of a bedaquiline and pretomanid backbone (BPa) in combination with one of three oxazolidinones. Arm 2 will study linezolid (BPaL) at a dose of 600 mg daily, Arms 3A and 3B will study TBI-223 at 1200 mg and 2400 mg daily, respectively, and Arms 4A and 4B will study sutezolid at 800 mg and 1600 mg daily, respectively. The primary efficacy objective is to compare sputum culture time to positivity (TTP) slope over the first 6 weeks of treatment for each experimental treatment arm to SOC. The primary safety objective is to compare new Grade 3 or higher adverse events over the first 8 weeks of treatment for each experimental treatment arm to SOC. After the intensive phase, all participants will receive the standard isoniazid and rifampicin (HR) continuation phase for 18 weeks and will be followed for 52 weeks after TB treatment initiation to assess long-term outcomes.
Discussion: Wave 1 of the RAD-TB platform aims to identify the optimal oxazolidinone(s), with regard to both efficacy and safety, to combine with the BPa backbone for the treatment of DS-TB. Subsequent waves of this platform trial may add a fourth drug to the regimen, study new diarylquinolines to substitute for bedaquiline, or study novel agents from other TB drug classes.
Trials registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT06192160. Registered on January 5, 2024, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06192160.
Keywords: TBI-223; bedaquiline; drug-susceptible; early efficacy; linezolid; platform trial; pretomanid; randomized controlled trial; sutezolid; time to positivity; tuberculosis.
Figures
References
-
- Fox W, Ellard GA, Mitchison DA. Studies on the treatment of tuberculosis undertaken by the British Medical Research Council tuberculosis units, 1946–1986, with relevant subsequent publications. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 1999;3(10):S231–79. - PubMed
-
- Iseman MD. Tuberculosis therapy: past, present and future. Eur Respir J. 2002;20(Supplement 36):S87–94. - PubMed
-
- Murray JF, Schraufnagel DE, Hopewell PC. Treatment of Tuberculosis. A Historical Perspective. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(12):1749–59. - PubMed
-
- WHO. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment - Drug-susceptible tuberculosis treatment. [Internet]. 2022. [cited 2024 Apr 16]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240048126 - PubMed
Publication types
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical