This is a preprint.
Assessment of Ventricular-Arterial Coupling in Early Stage Middle-Aged Hypertensives
- PMID: 40195989
- PMCID: PMC11975016
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6189873/v1
Assessment of Ventricular-Arterial Coupling in Early Stage Middle-Aged Hypertensives
Update in
-
Assessment of ventricular-arterial coupling in early stage middle-aged hypertensives.J Hum Hypertens. 2025 Aug;39(8):549-558. doi: 10.1038/s41371-025-01042-4. Epub 2025 Jul 8. J Hum Hypertens. 2025. PMID: 40628974
Abstract
Background: Ventricular-arterial coupling (VAC) is altered by aging and cardiovascular comorbidities, indicating myocardial dysfunction and/or arterial stiffness. Our aim was to demonstrate whether lifestyle changes and anti-hypertensive drug treatment would improve VAC in recently diagnosed, early stage middle-aged hypertensives (HTN) without organ damage.
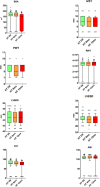
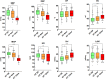
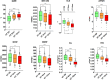
Methods: Arterial elastance (Ea), carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV), global longitudinal strain (GLS), and myocardial work (MW) [global work index (GWI), global constructive work (GCW), global wasted work (GWW), and global work efficiency (GWE)] were investigated. This retrospective observational study involved 126 individuals (mean age 40 years; 55% female), divided into HTN and normotensives, NT. Clinical, echocardiographic and echo vascular parameters were assessed. Lifestyle changes were recommended for HTN. If blood pressure (BP) values still remained high, anti-hypertensive drug treatment was administered.
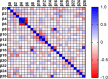
Results: Higher values of systolic blood pressure (SBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), GWI, GCW, and GWW were observed in HTN. By following lifestyle changes, BP [diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and MAP], HR, VAC, Ea, cfPWV, GWE, and GLS were changed in HTN; after 6 months of anti-hypertensive drug treatment, BP (SBP, DBP and MAP), HR, VAC, Ea, cfPWV, GWI, GCW, GWW, GWE, and GLS were found to be changed. VAC was linearly related to cfPWV and GLS at two follow ups. No statistically significant difference in VAC between HTN and NT was found.
Conclusions: Along with a decrease in BP, smoking cessation, and HR control highlighted a significant role in cardiovascular prevention by improvement of VAC, Ea, cfPWV, GLS and MW.
Keywords: arterial elastance; arterial hypertension; global longitudinal strain; myocardial work; pulse wave velocity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors affirm that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
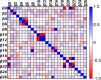
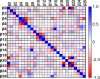
Similar articles
-
Assessment of ventricular-arterial coupling in early stage middle-aged hypertensives.J Hum Hypertens. 2025 Aug;39(8):549-558. doi: 10.1038/s41371-025-01042-4. Epub 2025 Jul 8. J Hum Hypertens. 2025. PMID: 40628974
-
Estimated Pulse Wave Velocity-to-Global Longitudinal Strain Ratio: A Tool for Differentiating Heart Failure Subtypes?Cardiology. 2025 May 23:1-11. doi: 10.1159/000546345. Online ahead of print. Cardiology. 2025. PMID: 40414215
-
Long-term cardiovascular consequences of cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction: insights from ventricular-arterial coupling and myocardial work.Eur Heart J Imaging Methods Pract. 2025 Jun 3;3(1):qyaf072. doi: 10.1093/ehjimp/qyaf072. eCollection 2025 Jan. Eur Heart J Imaging Methods Pract. 2025. PMID: 40584915 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial stiffness measured by pulse wave velocity correlated with cognitive decline in hypertensive individuals: a systematic review.BMC Neurol. 2024 Oct 16;24(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03905-8. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39415095 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for treating fibromyalgia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD007070. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007070.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vitali A, Zouein FA, Booz GW, Altara R. Prognostic Utility of Assessing Ventricular-Arterial Coupling in Arterial Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases. Minerva Cardiology and Angiology 2024–5. - PubMed
-
- Vitali A, Zouein F A, Booz G W, Altara R. Clinical Utility of Myocardial Work Assessment in Arterial Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases. Minerva Cardiology and Angiology 2024–5. - PubMed
-
- Kelly MS, Dacey A, Siana A, Ojeda J. Efficacy and Safety of a Polypill to Reduce Cardiovascular Events: A Review of Clinical Trials. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2024; 83(1): 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Wang L, Huang Y, Evans PC, Little PJ, Tian X, Weng J, Xu S. Anthocyanins in Vascular Health and Disease: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potential. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2024; 84(3): 289–302. - PubMed
-
- Chilbert MR, Woodruff AE, Rogers KC. A Practical Guide to Understanding and Treating Peripheral Artery Disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2024; 83(6): 565–579. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

