Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm and Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery (DACA) Aneurysms Related to Azygos and an Unusual Single Pericallosal Artery Variant: A Case Report
- PMID: 40196083
- PMCID: PMC11973609
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80219
Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm and Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery (DACA) Aneurysms Related to Azygos and an Unusual Single Pericallosal Artery Variant: A Case Report
Abstract
The authors describe the case of multiple rare distal anterior cerebral artery (DACA) aneurysms related to a middle cerebral artery (MCA) aneurysm, an azygos, and an undescribed anterior cerebral artery (ACA) anatomical variation. A 61-year-old woman in a severe clinical state was diagnosed with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) secondary to a ruptured anterior A3 DACA aneurysm. The patient also had unruptured kissing superior A3 DACA aneurysms, an atherosclerotic DACA aneurysm between the anterior and superior DACA aneurysms, and an unruptured MCA left aneurysm. Two pericallosal anatomical variations were seen: an A2 azygos and a rare single post-bifurcation (callosomarginal artery) pericallosal artery. All aneurysms were clipped using a single-staged left craniotomy with interhemispheric, subfrontal, and transsylvian access. This study demonstrates a patient with rare anatomical ACA variants and multiple complex aneurysms treated in a single-stage craniotomy.
Keywords: aneurysm; anterior cerebral artery variant; daca; mirror aneurysm; pericallosal artery.
Copyright © 2025, Chavez-Herrera et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
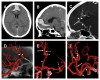
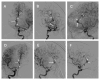
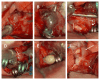
References
-
- Lehecka M, Dashti R, Lehto H, Kivisaari R, Niemelä M, Hernesniemi J. In: Surgical Management of Cerebrovascular Disease. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum. Vol. 107. Vienna: Springer; 2010. Distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms; pp. 15–26. - PubMed
-
- Anatomic features of distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms: a detailed angiographic analysis of 101 patients. Lehecka M, Porras M, Dashti R, Niemelä M, Hernesniemi JA. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:219–229. - PubMed
-
- Detailed description of the anterior cerebral artery anomalies observed in a cadaver population. Cilliers K, Page BJ. Ann Anat. 2016;208:1–8. - PubMed
-
- The change of location of the anterior cerebral artery in angiographic imaging [Article in German] Fischer E. Zentralbl Neurochir. 1938;3:300–312.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
