Predictive intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) parameters in the staging of fibrosis in hepatitis B patients
- PMID: 40196312
- PMCID: PMC11973707
- DOI: 10.5114/pjr/199686
Predictive intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) parameters in the staging of fibrosis in hepatitis B patients
Abstract
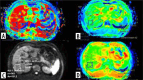
Purpose: Our aim was to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) parameters [D, D*, f, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values] in the detection and staging of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Material and methods: In this prospective study, a patient group of 64 consecutive patients (with a mean age of 43 years, 30 women and 34 men) with HBV, who scheduled liver biopsy, and a control group of 30 healthy individuals without liver disease underwent IVIM-DWI scan. A total of 94 IVIM-DWI examinations were analysed. IVIM-DWI parameters were measured in the right lobe of the liver. The IVIM-DWI parameters of the patient and control groups were compared by Mann-Whitney U test. The patient group was classified into subgroups according to fibrosis stage of histopathological results. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was conducted to assess the sensitivity and specificity of each parameter for detection and staging fibrosis.
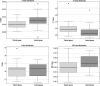
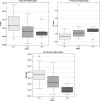
Results: D and ADC values were significantly lower in the patient group compared to the control group (p < 0.05), while D* values were significantly higher (p < 0.05). No significant difference was observed in f values between the 2 groups. D* had the highest diagnostic performance, with a sensitivity of 78.1% and specificity of 73.3%, with a cut-off value of 1.4 × 10-3 mm2/s in the differentiation of fibrosis stages.
Conclusions: IVIM-DWI, particularly the D, D*, and ADC parameters, is an adjunctive non-invasive alternative to biopsy in the staging of HBV-related liver fibrosis, especially for the prediction of advanced fibrosis.
Keywords: chronic hepatitis B; cirrhosis; diffusion-weighted imaging; fibrosis; intravoxel incoherent motion; magnetic resonance imaging.
© Pol J Radiol 2025.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluating the Histopathology of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Intravoxel Incoherent Motion-Diffusion Weighted Imaging Comparing With Diffusion-Weighted Imaging.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 23;11:670085. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.670085. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34249707 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-based staging of hepatic fibrosis: Comparison of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging with magnetic resonance elastography.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Jul;42(1):204-10. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24760. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25223820
-
Quantitative study of preoperative staging of gastric cancer using intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging as a potential clinical index.Eur J Radiol. 2021 Aug;141:109627. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109627. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Eur J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34126429
-
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Quantitative Differentiation of Breast Tumors: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 20;10:585486. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.585486. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194733 Free PMC article.
-
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Used to Detect Prostate Cancer and Stratify Tumor Grade: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 11;10:1623. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01623. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33042805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parola M, Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol Aspects Med 2019; 65: 37-55. - PubMed
-
- Karsdal MA, Hallsworth K, Scragg J, Leeming DJ, Villesen IF, Avery L, et al. . Serum levels of fibrogenesis biomarkers reveal distinct endotypes predictive of response to weight loss in advanced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Commun 2023; 7: e0254. DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000254. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jang W, Jo S, Song JS, Hwang HP, Kim SH. Comparison of diffusion-weighted imaging and MR elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2023; 48: 2763-2768. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
