This is a preprint.
SuperMetal: A Generative AI Framework for Rapid and Precise Metal Ion Location Prediction in Proteins
- PMID: 40196543
- PMCID: PMC11974720
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.21.644685
SuperMetal: A Generative AI Framework for Rapid and Precise Metal Ion Location Prediction in Proteins
Update in
-
SuperMetal: a generative AI framework for rapid and precise metal ion location prediction in proteins.J Cheminform. 2025 Jul 15;17(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13321-025-01038-9. J Cheminform. 2025. PMID: 40665445 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Metal ions, as abundant and vital cofactors in numerous proteins, are crucial for enzymatic activities and protein interactions. Given their pivotal role and catalytic efficiency, accurately and efficiently identifying metal-binding sites is fundamental to elucidating their biological functions and has significant implications for protein engineering and drug discovery. To address this challenge, we present SuperMetal, a generative AI framework that leverages a score-based diffusion model coupled with a confidence model to predict metal-binding sites in proteins with high precision and efficiency. Using zinc ions as an example, SuperMetal outperforms existing state-of-the-art models, achieving a precision of 94 % and coverage of 90 %, with zinc ions localization within 0.52 ± 0.55 Å of experimentally determined positions, thus marking a substantial advance in metal-binding site prediction. Furthermore, SuperMetal demonstrates rapid prediction capabilities (under 10 seconds for proteins with ∼ 2000 residues) and remains minimally affected by increases in protein size. Notably, SuperMetal does not require prior knowledge of the number of metal ions-unlike AlphaFold 3, which depends on this information. Additionally, SuperMetal can be readily adapted to other metal ions or repurposed as a probe framework to identify other types of binding sites, such as protein-binding pockets.
Keywords: Generative AI; diffusion model; metal-binding sites; metalloprotein.
Figures
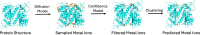
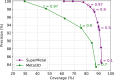
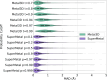
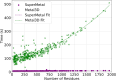
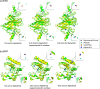
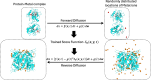
Similar articles
-
SuperMetal: a generative AI framework for rapid and precise metal ion location prediction in proteins.J Cheminform. 2025 Jul 15;17(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13321-025-01038-9. J Cheminform. 2025. PMID: 40665445 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shu Nanjiang, Zhou Tuping, and Hovmöller Sven. Prediction of zinc-binding sites in proteins from sequence. Bioinformatics, 24(6):775–782, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Andreini Claudia, Banci Lucia, Bertini Ivano, and Rosato Antonio. Counting the zinc-proteins encoded in the human genome. Journal of proteome research, 5(1):196–201, 2006. - PubMed
-
- McCall Keith A, Huang Chih-chin, and Fierke Carol A. Function and mechanism of zinc metalloenzymes. The Journal of nutrition, 130(5):1437S–1446S, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Berg Jeremy Mand Shi Yigong. The galvanization of biology: a growing appreciation for the roles of zinc. Science, 271(5252):1081–1085, 1996. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
