This is a preprint.
RAB5c controls the assembly of non-canonical autophagy machinery to promote phagosome maturation and microbicidal function of macrophages
- PMID: 40196584
- PMCID: PMC11974809
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.25.645097
RAB5c controls the assembly of non-canonical autophagy machinery to promote phagosome maturation and microbicidal function of macrophages
Abstract
Non-canonical conjugation of ATG8 proteins, including LC3, to single membranes implicates the autophagy machinery in cell functions unrelated to metabolic stress. One such pathway is LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP), which aids in phagosome maturation and subsequent signaling upon cargo uptake mediated by certain innate immunity-associated receptors. Here, we show that a specific isoform of RAB5 GTPases, the molecular switches controlling early endosome traffic, is necessary for LAP. We demonstrate that RAB5c regulates phagosome recruitment and function of complexes required for phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate [PI(3)P] and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by macrophages. RAB5c facilitates phagosome translocation of the V-ATPase transmembrane core, which is needed for ATG16L1 binding and consequent LC3 conjugation. RAB5c depletion impaired macrophage elimination of the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus and disruption of the V-ATPase-ATG16L1 axis increased susceptibility in vivo. Therefore, early endosome-to-phagosome traffic is differentially regulated to promote LAP and ROS contributes to resistance against A. fumigatus by effecting LAP.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; LC3-associated phagocytosis; Non-canonical autophagy; RAB5c GTPase.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
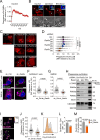
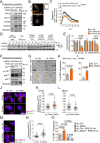
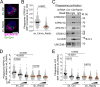
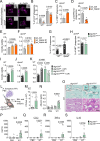
References
-
- Wang Y., Ramos M., Jefferson M., Zhang W., Beraza N., Carding S., Powell P.P., Stewart J.P., Mayer U., and Wileman T. (2022). Control of infection by LC3-associated phagocytosis, CASM, and detection of raised vacuolar pH by the V-ATPase-ATG16L1 axis. Sci Adv 8, eabn3298. 10.1126/sciadv.abn3298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akoumianaki T., Vaporidi K., Diamantaki E., Pène F., Beau R., Gresnigt M.S., Gkountzinopulou M., Venichaki M., Drakos E., El-Benna J., et al. (2021). Uncoupling of IL-6 signaling and LC3-associated phagocytosis drives immunoparalysis during sepsis. Cell Host Microbe 29, 1277–1293.e1276. 10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
