This is a preprint.
Rewired m6A methylation of promoter antisense RNAs in Alzheimer's disease regulates global gene transcription in the 3D nucleome
- PMID: 40196645
- PMCID: PMC11974732
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.22.644756
Rewired m6A methylation of promoter antisense RNAs in Alzheimer's disease regulates global gene transcription in the 3D nucleome
Update in
-
Rewired m6A of promoter antisense RNAs in Alzheimer's disease regulates neuronal genes in 3D nucleome.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 6;16(1):5251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60378-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40480976 Free PMC article.
Abstract
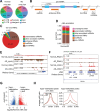
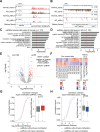
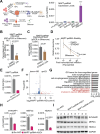
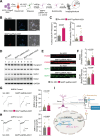
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent internal RNA modification that can impact mRNA expression post-transcriptionally. Recent progress indicates that m6A also acts on nuclear or chromatin-associated RNAs to impact transcriptional and epigenetic processes. However, the landscapes and functional roles of m6A in human brains and neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), have been under-explored. Here, we examined RNA m6A methylome using total RNA-seq and meRIP-seq in middle frontal cortex tissues of post-mortem human brains from individuals with AD and age-matched counterparts. Our results revealed AD-associated alteration of m6A methylation on both mRNAs and various noncoding RNAs. Notably, a series of promoter antisense RNAs (paRNAs) displayed cell-type-specific expression and changes in AD, including one produced adjacent to the MAPT locus that encodes the Tau protein. We found that MAPT-paRNA is enriched in neurons, and m6A positively controls its expression. In iPSC-derived human excitatory neurons, MAPT-paRNA promotes expression of hundreds of genes related to neuronal and synaptic functions, including a key AD resilience gene MEF2C, and plays a neuroprotective role against excitotoxicity. By examining RNA-DNA interactome in the three-dimensional (3D) nuclei of human brains, we demonstrated that brain paRNAs can interact with both cis- and trans-chromosomal target genes to impact their transcription. These data together reveal previously unexplored landscapes and functions of noncoding RNAs and m6A methylome in brain gene regulation, neuronal survival and AD pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- P01 AG066606/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG020670/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD107206/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA052769/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI077774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DK126138/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA246130/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM136922/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG059321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS093652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA200147/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG082132/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 GM132778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142704/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM138852/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL156059/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
